User:Kir/Bandsox
Prehistory and Peopling of Great Kirav
| “ | According to all known laws of anthropology, there is no way that Great Kirav should ever have been settled. The odds of modern man a) reaching and b) surviving in Great Kirav during the time periods currently deemed reasonable by the scholarly community, much less prospering there to the degree now believed, are beyond astronomical and require a suspension of disbelief too great for most Occidental scientists to even approach the topic. Kiravia, of course, exists anyway, because Kiravians don't care what Menquoi think is impossible. | ” |
| — B. Kinoflixin, Towards Ethnohistory - An Interdisciplinary Approach to Boreal Prehistory | ||
The distant past of Great Kirav is steeped in mythology and remains obscure. Archæological evidence suggest that the region may have been inhabited by modern man as early as 22,000 years ago, and subsequently beset with multiple waves of migration that have left enduring genetic, archæological, and cultural imprints on the island continent. The bulk of the genetic heritage of Kiravian peoples is attributable to an Ice Age migration from Levantia made possible by lower sea levels and dense floes of pack ice, with later contributions from the Ʒ-Q transoceanic migration and the still-unaccounted for progenitors of Haplogroup Ȼ.
Unravelling the truth of Kiravian prehistory and dark history is complicated by Coscivian culture's schizo-sacramentalist conception of reality (which does not clearly distinguish between what Occidental cultures would regard as the symbolic and the real) and its unique approach to time (which is often reflected in non-linear narratives and the confounding expression of temporal processes in spatial or virtual terms). This article will present the best current scientific understandings of Kiravian prehistory, contextualised by Kiravian traditional narratives and the research of dark philologists.
Pre-Human Times
Palaeozoic Era
Much of Great Kirav's plant biodiversity dates from clades attested from the Carboniferous through Permian periods.
Mesozoic Era

The Mesozoic Era of Great Kiravia, defined as an era as encompassing the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods on the continent of Great Kiravia, lasted from about 252 to 66 million years ago.[1] Often referred to as the "Age of Reptiles",[2] it is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, an abundance of gymnosperms (such as ginkgoales, bennettitales) and ferns, a hot greenhouse climate and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The period is defined geologically as beginning with the first appearance of the Conodont Hindeodus parvus and ending with an Iridium enriched layer associated with a major meteorite impact in modern-day Daxia and subsequent K-Pg extinction event. It is also sometimes referred to as the "Age of Conifers" in Great Kiravia due to the abundance of fossilized material from coniferous trees.[3]
Great Kiravia is unique in the Mesozoic for being an island continent with only very little outside contact following the Pangaea-Kiravia split at the end of the Triassic period.[4] With basal clades of pterosauromorphs, theropods, sauropodomorphs and ornithischians already inhabiting Great Kiravia at the time of the split however, these were able to evolve and diversify independently of archosauromorphs elsewhere, resulting in numerous examples of convergent evolution with otherwise very distantly related genera but also many examples of island gigantism, island dwarfism and notably of Bergmann's rule.[5] Evolution on the continent of Great Kiravia was heavily influenced by its three distinct biomes; a volcanic nearly arctic climate in the far north, a temperate highly arboreal climate in the south and a major riparian border zone in-between the two characterized by rolling plains and river deltas.[6]
Despite a relatively limited number of clades of synapsids, dinosauromorphs and pterosauromorphs occupying Great Kiravia following the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, the paleobiological diversity of Great Kiravia appears to be only slightly weaker than that of Sarpolevantia in the advent of the Cretaceous, suggesting a rapid and diverse evolutionary process had taken place during the Jurassic to fill all the niches left open by the T-J event.[7] At least one clade of small Kiravian theropods appear to have evolved powered flight independently of their Sarpolevantine counterparts during the late Jurassic period; there is also physical paleontological evidence of feathers in many theropods of various sizes in Great Kiravia, lending further evidence to the theory that feathers are ancestral to archosaurian reptiles.[8] Like the rest of the world, the Cretaceous period ended when the K-Pg extinction event occured following a major meteor striking central Daxia, causing the mass extinction of all non-avian dinosaurs and most other tetrapods weighing more than 25 kilograms (55 pounds).
Cenozoic Era
Earliest Homonids
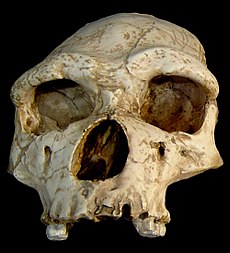
During the late 20th century AD, palæontologists unearthed skeletal remains of archæic humans present in Great Kirav during the middle Pleistocene, which were eventually concluded to represent two distinct species. The more anatomically archæic of the two, Homo vetus montanus, appear to have been sluggish, shuffling creatures; dull but hardy tundra-dwellers with a robust physique and limited cognitive and linguistic capabilities compared to the more anatomically "modern" H. darudensis. Although direct evidence is lacking, most palæontologists find it probable that both species were more hirsute than modern man, with ample body hair aiding their survival in the glaciated conditions of Pleistocene Kirav.
 |
 |
First Humans - Ice Bridges from Demomap

The present accepted consensus regarding the colonisation of Great Kirav by Homo sapiens sapiens maintains that the island continent was first peopled by a founder population of marine mammal hunters originating from the north-central Levantine mainland who migrated across pack ice in pursuit of prey until eventually reaching pockets of unglaciated land (now likely submerged) along the ancient southern and southwestern shores of Great Kirav. This theory is colloquially known as the "iceberg-hopping thesis" (Coscivian: xistoīoribakursa). This migration is believed to have occurred sometime between 19,500 BC and 18,500 BC, though the lower bound of this window is not definite and the upper bound could be as late as the first abrupt rise in global sea levels around 18,000-17,500 BC.
Dark historians generally identify the homeland of the Ice Age Levantine migrants with the mythological concept of Demomap. Although variously interpretable from the oral traditions of Coscivian and Urom communities as a place, time, or abstract state of being, Kapuśitic and Cuomo-Passaic-speaking peoples present Demomap as the intermediate location of their ancestors between their emergence from the Shadow Realm and their arrival in Kam, interpretable either as the physical world at large or Great Kirav specifically.[9] As such, the hypothesised pre-migration prehistory of the proto-Kiravians is known as the 'Demomappic Period'. The proto-Kiravians of the Demomappic Period are associated with a particular lithic technique (examples of which are portrayed here) with examples known from both Ilánova and finds in Kubagne, Yonderre and [LOCATION], Caergwynn, cited as the strongest archæological evidence of the iceberg-hopping hypothesis. During the Demomappic Period, the proto-Kiravians are currently believed to have interacted economically and reproductively with the Packer Culture of the Vandarch Basin but remained culturally distinct therefrom.
Deep Prehistory
Primitive Period - Cold and also Dark
The era of human habitation of Great Kirav from initial migration to the the commencement of the last glacial retreat around the middle of the 12th millennium BC, a range of roughly seven thousand years, is known as the Primitive Period, and is largely synonymous with the Kiravian Palæolithic. The human population of Great Kirav during this era is presumed to have been extremely sparse. Some studies from the 1980s-90s AD suggested that the Archæo-Cronan and Archæo-Levantine founder populations may have numbered as few as 70 and 100 people respectively. More recent works accept figures higher up in the hundreds or even low thousands as plausible, with the caveat that the vast majority of migrants' genetic lineages became extinct during the Primitive Period and are not ancestral to modern Kiravians. Whatever its size, almost the entirety of this population would have lived on lands that are now submerged, severely limiting what can be gleaned about this earliest phase of Kiravian prehistory from archæological remains. As such, almost nothing is known about this period from modern science, and almost all that is comes from a handful of excavations in Ilánova and South Kirav.
Environmental conditions during the Primitive Period are believed to have been exceedingly harsh. The island continent was almost entirely glaciated during this time, and prehistoric Kiravian populations would have clung to its habitable coastal fringes, eking out a marginal living from hunting, gathering, and fishing.

Convoīon Culture
The next archæological culture to develop out of the Demomappic, appearing by 17,600 BC, was the Convoīon Culture, known from a handful of sites in Ilánova. Convoīon exhibits a much more diversified toolmaking repertoire, utilising a wider range of materials than the stone-prone Demomappic to include hematite, worked animal bones, and other naturally-occuring substances. The dramatically more sophisticated tool inventories found at so few dig sites suggests a society much more advanced in its economy and comfortable in its surroundings than its Demomappic predecessors, migrating less frequently and availing themselves of more thitherto untapped food sources. The Convoīon Culture appears to have employed more specialized hunting, fishing, and collecting techniques, in contrast to the post-migration Demomappic generalist hunters. It is also the Convoīon culture that left the first unambiguous examples of rock art in Kiravia.
Society I (ca. 12,500 BC - ca. 9600 BC) - We Live in This
Come the Late Ice Age, glacial retreat and gradual warming of the climate allowed Kiravians to break out from their highly constrained High Ice Age mode of production, enabling population growth and the formation of societies beyond the scale of primitive bands.
This is a time of dramatic (but mostly good) change for Kiravians, whose material culture advanced considerably into what is known as the Lower Kiravian Epipalæolithic or the Society I Culture in response to major environmental shifts, beginning with a second abrupt rise in sea levels around 12,475 BC. This rise in sea levels effected the submersal of what were presumably the most heavily populated coastal areas of Kirav, but the glacial retreat responsible for it also opened up more inland areas to ecological colonisation and subsequent human habitation.
During the Late Ice Age, the continental ice sheet that had previously covered most of the continent contracted to the island continent's central basin, flanked by the Aterandic, Ximantav, and West Highlands ranges.
The people of the Society I culture formed somewhat larger social groups than their predecessors, and many communities lived as (at least seasonally-)sedentary food collectors, using markedly more sophisticated social organisation and lithic tools to extract sustenance from a wide variety of sources. Evidence of semi-permanent settlements and specialised tools disappears around the time of the Pleistocene-Holocene transition, suggesting that the Society I culture collapsed under pressure from major environmental changes, reverting to a smaller-scale hunter-gatherer lifestyle for several centuries.
[The Glacier and its lasting psychic effects]
Pleistocene-Holocene Collapse
The Middle Kiravian Epipalæolithic or Gameritic Upheaval was a time of dramatic (and mostly bad) change for Kiravians.
Natural cataclysms and their secondary environmental effects, namely disease and the disruption of essential food sources, caused the collapse of Society I and the abandonment of its characteristic permanent settlements. Most dark historians are of the opinion that the psychological and cultural impact of the Pleistocene-Holocene transition was incredibly traumatic, leaving a lasting impact on the Kiravian worldview.

Society II (ca. 9300 BC - ca. 8000 BC)
A second period of technological progress began during the late 9th millennium BC, giving rise to the Society II culture, another pre-agricultural culture of sedentary food collectors. Society II communities were larger and more permanently settled than those of Society I, exhibiter better adaptations for survival in more inland areas, and may have practised primitive forms of horticulture at later stages. Society II appears to have collapsed abruptly around 8300 BC, for reasons still unknown. The period during which Society II emerged is known as the Kiravian Upper Epipalæolithic.
Some dark historians believe that the first incarnation of the Coscivian Empire, a tribal confederation referred to in modern texts as the Lawful Commonwealth, arose during the latter half of Society II. Others believe it arose during Society I, whereas Occidental scholars and Coscivians of a more scientific bent hold that the Lawful Commonwealth (if historical at all) could not have formed before the Neolithic consolidation of simple farming societies.
Using their arcane ability to divine fully-fledged visions of lost civilisations from examination of pottery shards, archæologists have theorised that Society II settlements exhibited a remarkably high degree of social stratification for a pre-agricultural society, perhaps even practising slavery.
Akai Collapse (ca. 8000 BC)
See also: Kiravo-Akhai Origins Conspiracy Theory
The Akai Collapse, by convention, marks the beginning of the end of Deep Prehistory and the beginning of the beginning of Near Prehistory. This distinction is mainly of significance to dark philologists who place certain foundational events in Coscivian history, such as the formation of the Lawful Commonwealth at a much greater time depth than Occidental archæology permits, toward contemporaneity with Society I and/or Society II.
Near Prehistory (ca. 7000 BC - 2373 BC)
[Things get more real from here on.]
As the massive ice sheets that had covered the interior and northern coast of the island continent diminished and finally disappeared, prehistoric Kiravian tribes fanned out across the full breadth of Great Kiravia and gradually began to embrace sedentism a third time. This time, however, the exit from hunting and gathering would be made permanent by the discovery of agriculture in the form of the nutritious and delicious potato. The starchy tuber was first cultivated on the lower slopes of the south-western highlands between 7000 and 6000 BC. A separate farming culture centred on buckwheat cultivation and beekeeping emerged on the eastern coastal plain toward the end of that timespan.
At the dawn of agriculture, certain patterns of social organisation had already settled into prevailing norms across the island continent. Tribes, in the strict sense of the word, had replaced lower-level band societies in all but the most marginal and inhospitable locales. Kiravian tribes were structured according to segmentary lineages, most of which were already strictly patrilineal and patrilocal as all Coscivian peoples are today, though a minority (now conserved only in a few urom tribes) were matrilineal and/or matrilocal. At this stage it is presumed that all or most tribes permitted cross-cousin marriage, though the extent to which it may have been preferred (as in later stages of both Coscivian and urom societies) is not yet known. Due to the segmentary lineage reckoning of kinship, the demographic size of a typical Kiravian tribe during the early agricultural age is somewhat imprecise, but it can be estimated that the largest tribal orders of stable political (that is, military) significance claimed common descent no further back than five generations (to a single great-great-great-great-grandfather) and probably included between 1,000 and 3,000 people. However, the everyday lives of early agrarian Kiravians would have been lived largely within the confines of autonomous village communities within a larger tribe, with such villages comprising between 50 and 400 people. Among those communities who had adopted agriculture, communities were only semi-sedentary, practicing shifting cultivation of the slash-and-burn type, using fire to fertilise the mediocre soil covering most of the continent with the rich nutrients accumulated in its thick forest cover. As such, villages would periodically migrate within a localised ambit in search of virgin land as the cinder-enriched soils of one area were depleted. Stress on the land and the contraction of these ambits due to growing populations and the generational fission of villages is believed to have contributed to the period of heightened violence known as the Age of Blood.
Ʒ-Q Invasion
The Y-DNA haplogroups Ʒ and Q appear in the Kiravian gene pool around 7000 BC. Modern frequency distribution of these haplogroups correlates with two main variables: Proximity of subjects' ancestral home to the West Coast, and belonging to a traditionally Itaho-Atrassic-speaking ethnic group (such as Qihuxians, Ūtrans, West Coast Marine Coscivians). As such, the Ʒ-Q influx is most commonly attributed to a trans-oceanic migration from Crona or alternatively Vallos-Polynesia (a minority theory) as part of the wide-reaching dispersal of chiefly Audonian-origin peoples through the aforementioned regions beginning circa 8000 BC. Archæological and dark philological evidence points to this migration accelerating into a violent invasion of Kiravia by more advanced wandering Audonians that spread up and down the West Coast and inland therefrom until running up against early adoptors of potato-based agriculture, who were a closer match to the invaders militarily and enjoyed the advantage of highland geography in defending their homes.
Age of Blood
early agricultural Kiravians became embroiled in a state of endemic warfare, not unlike that which has been documented among other relatively high-density simple farming societies elsewhere.
Lawful Commonwealth
The geographic location of the nucleus of the Lawful Commonwealth is unknown and controversial. Virtually every macro-region of Great Kirav, along with Koskenkorva, has laid claim to the distinction.
Using the traditional narratives as a source, it would appear that the key military advantage ensuring the security of the Lawful Commonwealth was its primitive form of collective security: Lawful tribes were safe from attack than Lawless tribes because they could rely upon neighbouring Lawful tribes for assistance in a simple threat environment wherein numerical superiority was sufficient to guarantee victory. The deterrent effect of collective security allowed the Lawful tribes to become more populous as they were spared the extremely high death rates from warfare that afflicted the Lawless tribes, providing additional fighting-age men that galvanised the deterrent effect. It follows that the Lawful Commonwealth could only be defeated in toto by an adversary if a countervailing tribal alliance was able to assemble more fighters, which is what the sources say happened. The Great Law chant includes the narrative of the Lawful Commonwealth's demise as an apologetic for its model of governance, essentially saying that its only flaw was that it worked too well, allowing the Lawful tribes to raid and displace the Lawless tribes further and further until the retreating Lawless tribes formed a grand alliance to counterattack and overwhelm the outer villages of the Commonwealth, after which the inner villages, being unprepared for war, fell swiftly. The Commonwealth was dissolved and Emperor Akˣɛ died a glorious and noble death in battle, but, the Chant says the scattered survivors of the Lawful tribes "carried the Law with them to the three corners of the Land."
Proto-Cities and Proto-States
The Age of Blood drew down as rates of endemic violence declined. Orthodox historians attribute this to the diffusion of norms that had proven advantageous to the Lawful Commonwealth outward beyond its direct sphere of influence, even continuing after its demise, as the Great Law Chant states (see above), enabling the formation of other higher-order proto-states and the pacification of larger pockets of territory, as well as the gradual abandonment of ultraviolent practices by tribes outside of these proto-states. More critical historians question whether the Lawful Commonwealth was truly the originator of the Four Rites and Four Precepts, or merely one of many adoptor societies of constructive innovations that arose elsewhere. What is certain is that multiple [prefix]lithic polities would claim the legacy of the Lawful Commonwealth, adopting its foundational narratives to legitimise their own rule and absorbing its laws as part of their own culture and custom.
The end of the Age of Blood allowed for the formation of more permanent settlements and larger-scale (though still thoroughly tribal) social organisation.
Megalithic Societies
Transition to Deep History
Open Questions
Wanderer Migrations
Post-Glacial Trans-Kilikas Contact
Wanderer Migration (The D)


| Form I - istuv | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Ergative | istuk | istuyak | ||
| Genitive | istul | istuyá | ||
| Indirect | istum | istuyam | ||
| Absolutives | ||||
| Number | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Aspect | Imperfect | Perfect | Imperfect | Perfect |
| Present | istuv | istuvi | istuya | istuyi |
| Past | istuve | istuvéi | istuyave | istuyavéi |
| Future | istuvo | istuvói | istuyavo | istuyavói |
| Jussive | istuvu | istuvúi | istuyavu | istuyavúi |
| Form II - rona | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Ergative | ronak | ronæk | ||
| Genitive | roná | ronæ | ||
| Indirect | ronam | ronám | ||
| Absolutives | ||||
| Number | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Aspect | Imperfect | Perfect | Imperfect | Perfect |
| Present | rona | ronavi | ronáv | ronávi |
| Past | ronave | ronavéi | ronáve | ronávéi |
| Future | ronavo | ronavói | ronávo | ronávói |
| Jussive | ronavu | ronavúi | ronávu | ronávúi |
| Form III - vālin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Ergative | vālith | vālinyak | ||
| Genitive | vālisk | vāliskya | ||
| Indirect | vālint | vālintya | ||
| Absolutives | ||||
| Number | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Aspect | Imperfect | Perfect | Imperfect | Perfect |
| Present | vālin | vālini | vālinyav | vālinyavi |
| Past | vāline | vālinéi | vālinyave | vālinyavéi |
| Future | vālino | vālinói | vālinyavo | vālinyavói |
| Jussive | vālinu | vālinúi | vālinyavu | vālinyavúi |
| Form III - kenor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Ergative | kenorth | kenoryak | ||
| Genitive | kenorsk | kenorskya | ||
| Indirect | kenord | kenordya | ||
| Absolutives | ||||
| Number | Nonplural | Plural | ||
| Aspect | Imperfect | Perfect | Imperfect | Perfect |
| Present | kenor | kenorsti | kenoryav | kenoryavi |
| Past | kenorste | kenorstéi | kenoryave | kenoryavéi |
| Future | kenorsto | kenorstói | kenoryavo | kenoryavói |
| Jussive | kenorstu | kenorstúi | kenoryavu | kenoryavúi |
- ↑ All times given by the Gregorian calendar unless otherwise stated.
- ↑ A term coined by Bergendii polymath Gideon-Raphael Mantelleaux in 1843.
- ↑ Balboa, Maximus: A comprehensive history of paleontology, pg. 3. 2004.
- ↑ The exception being marine reptiles and intercontinental ocean-going pterosaurs like Quetzalcoatlus.
- ↑ Bergmann's rule, named for Yonderian paleontologist Hieronymous Bergmann, states that populations and species of larger size are found in colder environments, while populations and species of smaller size are found in warmer regions.
- ↑ Konsaháken, Vurdhan: Paleogeology of Great Kiravia, University of Belarus, pg. 14-19. 2012.
- ↑ Lyukquar, Ansar: Kiravia and the Mesozoic, pg. 67-69. 2015.
- ↑ Balboa, Maximus: A comprehensive history of paleontology, pg. 104. 2004.
- ↑ In the narratives of Transkiravian-speaking peoples such as the Kir, Demomap is equated to Ixnaī, though the mythological significance of Ixnaī is somewhat different.