Southern Route: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary Tag: 2017 source edit |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
The outsourcing of colonial administration of the [[Stenza]] territory to the [[South Seas Development Company|South Seas Trading Company]] and the expansion of its commercial activities by establishing bases in Port Bondor, Rakin (later Rakahanga) and Ambo led to the establishment of a quasi commercial monopoly on the western end of the Southern Route. As the company's wealth increased, it would outfit a fleet of warships of its own, nominally under Imperial control but in practice operating to protect company commercial interests. The [[Harmonious Flotilla Invincible]] began operating in 1758, when it fended off Bergendii corsairs off the coast of [[Freda Island]]. | The outsourcing of colonial administration of the [[Stenza]] territory to the [[South Seas Development Company|South Seas Trading Company]] and the expansion of its commercial activities by establishing bases in Port Bondor, Rakin (later Rakahanga) and Ambo led to the establishment of a quasi commercial monopoly on the western end of the Southern Route. As the company's wealth increased, it would outfit a fleet of warships of its own, nominally under Imperial control but in practice operating to protect company commercial interests. The [[Harmonious Flotilla Invincible]] began operating in 1758, when it fended off Bergendii corsairs off the coast of [[Freda Island]]. | ||
===Economic and social impact=== | ===Economic and social impact=== | ||
====In Daxia==== | |||
The impact of the establishment of the southern route was enormous in both economic and cultural terms for the Daxian. The flow of trade goods greatly enrichened the Qian state, with the treasury benefiting from extra taxes and tariffs, including a tax on all precious metals, fees for providing naval protection to merchant ships, docking, warehouse uses and clerical services. In addition there were cultural and technological exchanges, with several sarpedonian scholars taking up employment with the Daxian. One such case was mathematician and astronomer Justo Barbajan, who worked at the Qian court as Director of the Imperial Observatory. The first Christian preachers arrived by boat in 1623, with one of them eventually founding what would become the [[Democratic Christian Church of Daxia and the East]]. | |||
==== In Pelaxia==== | |||
On May 17, 1615, the fleet reached Daxia, thus having established the route via the Cathay Ocean and managing to open the sea route Sarpedon to Alshar. Negotiations with the local Qian State were difficult. Pogiano's efforts to obtain favorable commercial terms have been hampered by the different cultures and the low value of their gifts – in the East it was customary for kings to offer presents to the foreign envoys; in the West the kings were expected to be impressed with rich offerings. Goods presented by the Pelaxian proved insufficient to impress the Daxian and representatives mocked their offers. Pogiano's perseverance made him nevertheless initiate negotiations between him and the Qian's, who were pleased with the letters of King Eladio I. Finally, Pogiano managed to get an ambiguous letter of concession rights to trade and an enclave on the coast managed by a Pelaxian governor. | |||
[[File:Casa del Alshar.jpg|thumb|Palacio de la Costa (on the right), where the Casa del Alshar was headquartered, and its naval yards (on the left), in 1675.]] | |||
Pelaxian would be at first a crown monopoly. The monopoly had been managed by the Casa del Alshar, the royal trading house founded around 1650, it was the first to start a joint stock company to trade in Alshar. The Casa was responsible for the maintenance of a yearly commercial fleet and armada. However, by 1660, the Casa's finances were in dire straits and in 1670, the King of Pelaxia issued a decree opening up trade to Pelaxia to any private Pelaxian and Cartadanian national. As few took up the offer, the free trade decree was replaced in 1678 by a new system of annual monopolies, where the Casa sold Alshar trading contracts to a private Pelaxian merchant consortium, granting them a monopoly for one year. This annual contract system was abandoned in 1697, and the royal monopoly resumed. | Pelaxian would be at first a crown monopoly. The monopoly had been managed by the Casa del Alshar, the royal trading house founded around 1650, it was the first to start a joint stock company to trade in Alshar. The Casa was responsible for the maintenance of a yearly commercial fleet and armada. However, by 1660, the Casa's finances were in dire straits and in 1670, the King of Pelaxia issued a decree opening up trade to Pelaxia to any private Pelaxian and Cartadanian national. As few took up the offer, the free trade decree was replaced in 1678 by a new system of annual monopolies, where the Casa sold Alshar trading contracts to a private Pelaxian merchant consortium, granting them a monopoly for one year. This annual contract system was abandoned in 1697, and the royal monopoly resumed. | ||
The Carto-Pelaxian Commonwealth of 1618, changed little at first. However, the increasing influence of Levantine trading companies in the Alshari continent after 1698 led the Commonwealth to experiment with different arrangements to secure the new born colonial empire. In 1605, he created the Oficina del Alshar, to bring affairs in Commonwealth Alshar under closer supervision of the Parliament. But this conflicted with older lines of Carto-Pelaxian authority, and the council was eventually dissolved in 1714. | The Carto-Pelaxian Commonwealth of 1618, changed little at first. However, the increasing influence of Levantine trading companies in the Alshari continent after 1698 led the Commonwealth to experiment with different arrangements to secure the new born colonial empire. In 1605, he created the Oficina del Alshar, to bring affairs in Commonwealth Alshar under closer supervision of the Parliament. But this conflicted with older lines of Carto-Pelaxian authority, and the council was eventually dissolved in 1714. | ||
====In Puertego==== | |||
====In Stenza==== | |||
[[Category:Daxia]] | [[Category:Daxia]] | ||
[[Category:Pelaxia]] | [[Category:Pelaxia]] | ||
Revision as of 13:29, 5 June 2023
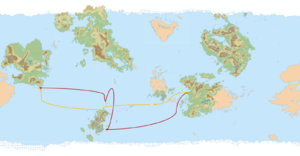
The Southern Route, also commonly known as the South Alshar-Sarpedon sea route is a shipping route from the Daxian southeastern coast, through the Ocean of Cathay and on to the Kindreds Sea and Pelaxian and Puertegan ports. The first recorded complete voyage of the route was made in 1615 by Gabo de Pogiano, an explorer and adventurer from the Carto-Pelaxian Commonwealth who started his trip on the port of Albalitor on the Kindreds Sea and came into contact with the Daxian Qian dynasty in Port Bondor, Zhijun. Impetus for developing alternate trade routes gained traction and support at the Qian court mainly as a way to evade the Burgoignesc monopoly on all Audonian sea routes, especially from its outpost on the island of Ayermer. The route would become more profitable to traverse in the early 17th century after the Qian colonization of Stenza by the South Seas Trading Company. In the modern era the route continues to be an important lane for Daxia and international marine shipping and several national navies operate throughout its whole length to provide security.
History
See Also: Pelaxian discovery of the sea route to Alshar
Background


Historically, sea exploration by Daxian dynasties was severely lacking in comparison to Levantine powers such as Burgundie. Most of Daxian trading with its neighbours was conducted through overland routes, rivers or by sea shipping that stuck close to the coastline. Burgundie's possession of islands controlling access to important waterways in Audonia such as Salarive and Antilles and its sometimes predatory attitudes, the dangers posed by Audonian pirates and high tariffs made trade through Burgoignesc controlled waters a fairly unappealing prospect. The discovery of Zhijun and later Stenza by an expedition commissioned by Emperor Yuanjian of the Qian dynasty opened the possibility of further lands yet to be discovered. Admiral Xi Haifong proceeded to conquer the Stenzan polynesian tribes and established the port of Xiwang there in 1613. The arrival in 1615 of Carto-Pelaxian explorer Gabo de Pogiano at Zhijun's Port Bondor confirmed to the Qian the existence of lands further east to trade with. Gabo de Pogiano established a rapport with the governor of Zhijun and was allowed to sail to Daxia alongside the Grog Fleet for an audience with imperial authorities.
Spices were always considered the gold of the of Polynesia and Alshar. Cinnamon, ginger, cloves, black pepper and turmeric had long been products which were difficult to obtain in Sarpedon and brought in by caravans and experienced merchants coming from Caphiria.
A merchant of Albalitor describes the overland spice route as follows: Only the markets of Venceia then scattered these spices all over Sarpedon, great in cost, and without guaranteed arrival. In 1300s, with the establishment of the Third Empire, the trade from Vencia reduced to a great degree due to the an increase of Coscivian piracy around Sarpedon. The advantage of the Pelaxians to establish a sea route therefore virtually free of assault – however, covered in perils in the sea – showed itself rewarding and outlined a large income to the Crown in the future. Pelaxia directly linked the spice producing regions to their markets in Sarpedon.
In March 1603, Pogiano was at the head of an expedition that weighed anchor from Albalitor. Under his control were three ships: the galleon Jesús María, of 600 tons and 30 cannons, Nuestra Señora de la Visitación and Nuestra Señora de las Mercedes. The expedition was entrusted by the King Jerónimo l, to suppress the incursions of Coscivian privateers in the seas to the south of Loa Republic.
Historians conjecture that they penetrated to a latitude of (64° S) in the Okatian Sea, and made port in the Freda Island. If correct, this would be the farthest south that anyone had travelled, at that time. Subsequently, several merchant vessels reported being blown south of 60° S in severe weather.
Around the year 1611, Pogiano attempted to undertake an exploration of the beyond Australis, and gathered information about an almost legendary Qian's Daxia, whose kingdom was located far to the west in Alshar, and sailed to it reaching it in 1615.
Establishment
Gabo de Pogiano's 1615 journey became an embassy after contact with the Daxian. After arriving in the port of Zong on the 10th of October, he had an audience with Digen Youdu, Viceroy of Ganshu; with whom he negotiated an agreement that allowed him to dock in Daxian ports and engage in trade, map out the surrounding seas and build a fort in the Tanhai coastal commandery. Pogiano in turn committed himself to on his return trip, guide a Qian squadron to the Kindreds Sea and the coast of Sarpedon. The ships that would join him on Zhijun were the Falun, the Gong and the Shen Yun; the first Daxian ships to ever make it to Sarpedon. Later contacts with Acirien representatives would lead to a similar agreement. The Qian would send goods such as sugarcane, barrels of slozo, pink salt, ebony wood and cinnamon and in return would receive (insert Sarpedonian products such as wine)
The outsourcing of colonial administration of the Stenza territory to the South Seas Trading Company and the expansion of its commercial activities by establishing bases in Port Bondor, Rakin (later Rakahanga) and Ambo led to the establishment of a quasi commercial monopoly on the western end of the Southern Route. As the company's wealth increased, it would outfit a fleet of warships of its own, nominally under Imperial control but in practice operating to protect company commercial interests. The Harmonious Flotilla Invincible began operating in 1758, when it fended off Bergendii corsairs off the coast of Freda Island.
Economic and social impact
In Daxia
The impact of the establishment of the southern route was enormous in both economic and cultural terms for the Daxian. The flow of trade goods greatly enrichened the Qian state, with the treasury benefiting from extra taxes and tariffs, including a tax on all precious metals, fees for providing naval protection to merchant ships, docking, warehouse uses and clerical services. In addition there were cultural and technological exchanges, with several sarpedonian scholars taking up employment with the Daxian. One such case was mathematician and astronomer Justo Barbajan, who worked at the Qian court as Director of the Imperial Observatory. The first Christian preachers arrived by boat in 1623, with one of them eventually founding what would become the Democratic Christian Church of Daxia and the East.
In Pelaxia
On May 17, 1615, the fleet reached Daxia, thus having established the route via the Cathay Ocean and managing to open the sea route Sarpedon to Alshar. Negotiations with the local Qian State were difficult. Pogiano's efforts to obtain favorable commercial terms have been hampered by the different cultures and the low value of their gifts – in the East it was customary for kings to offer presents to the foreign envoys; in the West the kings were expected to be impressed with rich offerings. Goods presented by the Pelaxian proved insufficient to impress the Daxian and representatives mocked their offers. Pogiano's perseverance made him nevertheless initiate negotiations between him and the Qian's, who were pleased with the letters of King Eladio I. Finally, Pogiano managed to get an ambiguous letter of concession rights to trade and an enclave on the coast managed by a Pelaxian governor.

Pelaxian would be at first a crown monopoly. The monopoly had been managed by the Casa del Alshar, the royal trading house founded around 1650, it was the first to start a joint stock company to trade in Alshar. The Casa was responsible for the maintenance of a yearly commercial fleet and armada. However, by 1660, the Casa's finances were in dire straits and in 1670, the King of Pelaxia issued a decree opening up trade to Pelaxia to any private Pelaxian and Cartadanian national. As few took up the offer, the free trade decree was replaced in 1678 by a new system of annual monopolies, where the Casa sold Alshar trading contracts to a private Pelaxian merchant consortium, granting them a monopoly for one year. This annual contract system was abandoned in 1697, and the royal monopoly resumed.
The Carto-Pelaxian Commonwealth of 1618, changed little at first. However, the increasing influence of Levantine trading companies in the Alshari continent after 1698 led the Commonwealth to experiment with different arrangements to secure the new born colonial empire. In 1605, he created the Oficina del Alshar, to bring affairs in Commonwealth Alshar under closer supervision of the Parliament. But this conflicted with older lines of Carto-Pelaxian authority, and the council was eventually dissolved in 1714.