Pelaxia
This article is a work-in-progress because it is incomplete and pending further input from an author. Note: The contents of this article are not considered canonical and may be inaccurate. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. |
The Federal Republic of Pelaxia República Federal de Pelaxia | |
|---|---|
Motto: Unitum facimus fortitudinem | |
Anthem: None | |
 Pelaxia in Sarpedon | |
| Capital | Albalitor |
| Official languages | Pelaxian |
| Recognised regional languages | Latin, Savrian and Insuo Loa |
| Demonym(s) | Pelaxian |
| Government | Parliamentary Federal Republic |
• Federal Chancellor | Matías Mexes |
• Prime Minister of the Federal Republic | Pedro Meireles |
| Establishment | |
• Kingdom of Pelaxia | 1485 |
• Republic of Pelaxia | 1852 |
• Federal Republic of Pelaxia | 1876 |
| Area | |
• | 1,527,989 km2 (589,960 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 219,610,000 |
• Density | 143/km2 (370.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | NSD$6,072,828,138,000 |
• Per capita | NSD$28,165.8 |
| HDI (2017) | very high |
| Currency | Salia ($Sl) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .plx |
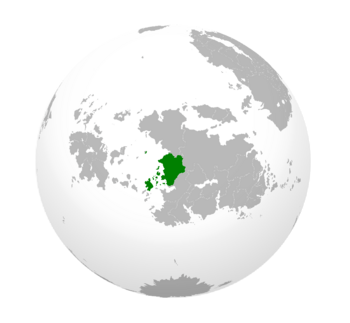
Pelaxia [pelaheea], officially the Federal Republic of Pelaxia, is a nation in the north west of Sarpedon. Pelaxia is located in Western Sarpedon It shares its northern borders with Cartadania, borders Caphiria at the East and shares its southern border with Grajnidar. Its coast rests on the Kindred Sea. In 2025 a series of unpopular socio-economic measures promoted by the recent right-wing government led to a popular uprising. This would be known as the Pelaxian Revolution.
With an area of 1,527,989 square kilometres, Pelaxia is the seventh largest country by area. Pelaxia is the flattest, and most humid inhabited valley, with the most fertile soil in the continent. It is a megadiverse country, and its latitude gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with tropical rainforests in the north-west, subtropical plains in the centre and south, and steppes with mountain ranges in the west.
Politically, Pelaxia is a federal parliamentary republic, comprising 29 provinces, autonomous communities and territories. Pelaxia's population of nearly 220 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the western seaboard.Albalitor is the nation's capital, while the largest cities are Villa Delfia, Agrila, Montia, Jojoba, and Jazmín. Pelaxia's abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade relations are crucial to the country's economy, which generates its income from various sources including services, crude oil exports, banking, manufacturing, agriculture and international education.
Anatomically modern humans first arrived in the Pelaxia Valley around 42,000 years ago. The first cultures and peoples that developed in current Pelaxian territory were Pre-Caphirian peoples such as the ancient Cognatish. Later, foreign Sarpedonian peoples such as the Kosalis developed coastal trading colonies. From the year 218 BCE, with the taking of the city of Augurias, the Caphirian colonization of Pelaxia began and, they quickly controlled the territory of present-day Pelaxia. The Caphirians had driven the Kosalis out of the valle by 206 BCE, and divided it into two administrative provinces. The Caphirians laid the foundations for modern Pelaxian culture and identity, and was the birthplace of important Caphirian generals.
Pelaxia is a highly developed country with a high-income economy; it has the world's thirteenth-largest economy, twelveth-highest per capita income and twentyfifth-highest Human Development Index. Pelaxia is a regional power, and has the world's thirteenth-highest military expenditure. Pelaxia ranks highly in quality of life, democracy, health, education, civil liberties, safety, and political rights, with all its major cities faring exceptionally in global comparative livability surveys.
It is a member of international groupings including the League of Nations, the E4, and Union of Sarpedonian States. Pelaxia maintains the "Pelaxian welfare model" with comprehensive social security system, and its values are rooted in egalitarian and marxist ideals. The Pelaxian state has large ownership positions in key industrial sectors, having extensive reserves of petroleum, natural gas, minerals, seafood, and fresh water. The petroleum industry accounts for around a quarter of the country's gross domestic product (GDP). On a per-capita basis, Pelaxia is Sarpedon's largest producer of oil and natural gas.
Pelaxian art, music, literature and cuisine have been influential worldwide, particularly in Northern Sarpedon. As a reflection of its large cultural wealth, Pelaxia has the world's fourth-largest number of World Heritage Sites and is the world's fifth-most visited country.
Etymolgy
"Pelaxia" derives from the latin word "Pelagia", which "pertains to the open sea", in reference to the Kindred Sea where the Pelaxian Coast lies.
History
See also:History of Pelaxia
The history of Pelaxia dates to the Antiquity when the pre-Caphirian peoples of the Kindred coast of the Pelaxian Valley made contact with the Kosalis and the first writing systems known as Paleopelaxian scripts were developed. In 1485, Jerónimo De Pardo, the Grand Duke of Agrila, unified Pelaxia as a dynastic union of disparate predecessor kingdoms ; its modern form of a republic was established in 1852. After the completion of the Union of Termia, the Crown began to explore across the Kindred Sea, expanding into Vallos and marking the beginning of the Golden Age under the Pelaxian Empire. Until the 1750s, Garza Pelaxia was the one of most powerful states in Sarpedon. During this period, Pelaxia was involved in all major Sarpedonian Wars, including the Kindred Wars. Pelaxian power declined in the latter part of the 18th century.
In the early part of the 19th century, most of the former Pelaxian Empire overseas disintegrated. A tenuous balance between liberal and conservative forces was struck in the establishment of a republic in Pelaxia; this period began in 1852 and ended in 1922. Then came the dictatorship of General Benedicto Álvaro Camargo (1922-1932). His government inaugurated a period ruled by a militarist party, the Restauración Nacional Party, up until 1957. From 1922 the country experienced rapid economic growth in the 1940s and early 1950s. With the death of Federico Pedro Olmos in November 1956 Pelaxia returned to the Federal Republic. With a fresh Constitution voted in 1958.
-
Cognatish statuette
-
Jerónimo I of Pelaxia "the Edifier"
-
Jerónimo III, Emperor of Carto-Pelaxia
-
Raul Solís, first Prime Minister of the Federation.
Antiquity (700 BC - 300 AD): The foundation of Pelaxia's history lies in Antiquity, with the emergence of pre-Caphirian Kindred coast dwellers engaging with Kosalis and developing early writing systems known as Paleopelaxian scripts. The Cognati, residing on the western Sarpedonian coast, displayed dual meanings in ancient texts - encompassing both valley inhabitants and specifically those along the western and southern shores. Cognatish language prevailed from the 7th to the 1st century BC, defining a stratified society with rulers, nobles, priests, artisans, and slaves. A senate of nobles convened, supported by a "fides" obligation system upheld by kings or chieftains. Vallosi influences like wine and olives were embraced, and metalwork thrived, yielding exceptional iron weaponry. The conquest era began around the 4th century BC with Caphirian General Ottiano's campaign, culminating in the annexation of Montia. Dividing valleys into Pelagia Orientis and Pelagia Occidentis, Cognati's later revolts were quelled. Caphiria further expanded by subduing Albalitoria and Cognatilitoria, concluding with the Litorian Wars' culmination in 16 BC.
Caphirian Recession and Kosal Expansion (300 AD - 484 AD): Internal conflicts within the Caphirian Republic, led by figures like Luccino Capontinus and Iscallio Maristo, triggered a five-year civil war known as the War of the Republic around the mid-5th century AD. The Republic suffered 120,000 casualties, causing its imminent collapse. Concurrently, the Caphirian hold over Pelaxia waned as four Sarpedonian tribes crossed the Cazuano river in 407, leading to the establishment of separate kingdoms - Losa in Montia, Ladri in the south, and Klis in Albalitore. Despite Caphirian attempts, these territories remained mostly beyond their control.
The Agrila Kingdom (5th - 8th centuries): Emerging as a successor state to Caphirian influence, the Agrila Kingdom occupied western Pelaxia from the 5th to the 8th centuries. Founded by Kosali settlers under King Magda, it stood independently from the Caphirian Empire's authority. Under King Evaristo, Kosali influence expanded, marked by their victory over the Caphirian armies at Cakia in 479. The defeat led to Caphirian attempts to curb expansion. Subsequently, the Kosali Kingdom of Albalitor arose in 618, expelling Klis from its capital and engaging with Rastri and Rati settlements. This era witnessed increasing unity between the Cognatish-Caphiravian populace and Kosal, often accompanied by persecution of outsiders. The Kosali Code, developed in the 7th century, became a bedrock for Pelaxian law during the Middle Ages.
Caphirian Reconquest (500 - 1485): This period witnessed the ascendancy of Catholic Kosali nobles who established feudal systems, leveraging monasteries and bishoprics to consolidate power. These Kosali leaders, characterized as partially Caphirianized, defended against Ladri, Rati, Losa, and Rastri incursions. The Edict of Agrila issued in 1180, which formally designated Sebastián Pasillas Castrillón as the Despote of Cognata and moved his royal seat to Albalitor. This historic decree signaled a turning point in the history of both Caphiria and Pelaxia, solidifying the Castrillón rule over the Pelaxian Valley after supressing the Kazofort Rebellion, a factor of stability which could rid the imperial administration of the management of a territory with endemic troubles. Pasillas clearly inherited his grandfather's splendor and his desire for recognition beyond his borders. Internally, he tried to satisfy both his Caphiravian and Kosali subjects and was divided between his religious capital, Venceia, and his “little Venceia”, Albalitor. He also undertook the major project of raising the ramparts of his historic capital and extending it to the new northern district. The Castrillón dynasty's 12th-century rise led to the establishment of cities like Alimoche, Fatides, and Barcegas. Concurrently, the Castrillóns expanded their influence, absorbing southern territories and forming alliances. The Montian Confederacy emerged as a political entity during this time, uniting various provinces under its banner. The 14th century witnessed a shift from feudalism to late medieval politics, with the Castrillóns vying against Agrila and Sebardoba for control. Battles and alliances reshaped the geopolitical landscape. In 1469, Despotes Mauhtémoc Castrillón's involvement in the Termia region led to conflicts, including pivotal battles like Alcoy and Jumilla. The fall of Tristán Castrillón in 1477, in which the Montian Confederacy played a role, marked a turning point, signaling the decline of the Castrillón dynasty and the realignment of power dynamics in the region.
Great Caphiravian Kingdom of Pelaxia (1485 - 1618): Marked by the Union of Termia in 1485, Pelaxia's history saw the rise of the House De Pardo dynasty through a marriage alliance between Reginaldo Castrillón and Jerónimo De Pardo. This union aimed to create a unified state governed by Albalitorian law, supported by the Montian Confederacy. The Jeronimian period fostered a blend of feudal and mercantile dynamics, with the Cortes Regium of 1516 shifting legislative power to the Corte General, initiating the "Golden Liberty" era characterized by aristocratic rule. The dynasty's reign from 1686 to 1802 was a prosperous era of cultural growth. Economically, Pelaxia relied on agricultural production through serfdom, diverging from Levantia's emerging capitalist trends. The 16th-century agricultural trade boom, coupled with peasant labor, fueled a profitable folwark economy. Mining and metallurgy thrived, contributing to commercial advancement. Exports via Albalitor, a prominent trade hub, maintained positive trade balances. Other towns like Agrila, Montia, and Fegona participated in transit and exports, with Albalitor's prominence driving its wealth and autonomy.
Carto-Pelaxian Commonwealth and the Pelaxian Empire (1632 - 1795): The establishment of the Carto-Pelaxian Commonwealth in 1618 through the Union of Alahuela followed the Great Schism of 1615 and the subsequent dissolution of the Southern Provinces. Notably, Pelaxia emerged as the dominant partner in the union, with its ruler ascending as the crowned Emperor of the federative monarchy. The Commonwealth's distinctive political structure featured a system of checks on monarchical power, exemplified by the Concilii Regii legislature controlled by the nobility. This innovative approach foreshadowed principles of modern democracy and constitutional monarchy. Ethnically diverse and religiously tolerant, the Commonwealth safeguarded religious freedom through the Albalitor Confederation Act of 1673. While Catholicism held the status of the "dominant religion" according to the 1791 Constitution, freedom of religion was maintained. However, the Commonwealth faced partitions due to the First Partition in 1772 and the Second Partition in 1793, ultimately leading to its dissolution through the Third Partition in 1795.
First Republic (1804-1814): The First Republic was a defining era in Pelaxian history, marked by the overthrow of the Girojón monarchy and the establishment of a triumvirate governance structure. This period emerged from a culmination of societal discontent and revolutionary fervor against perceived autocracy and economic disparities under the Girojón dynasty. The monarchy was toppled in a coordinated 1804 coup led by military figures and civic republican intellectuals. This marked a radical shift in Pelaxia's political landscape. The triumvirate that ensued featured key figures representing distinct ideologies. Collectively, the triumvirs enacted broad changes. They established a new constitution enshrining civil liberties and representative governance, while fostering an educated populace. Economic policies prioritized land reform, trade, and infrastructure. However, internal divisions and external pressures challenged the triumvirate's unity. By 1814, these factors, along with regional conflicts and economic hardships, led to the triumvirate's dissolution. This marked the end of the First Republic era and paved the way for the Girojón Restoration.
Girojón Restoration (1814 - 1852): The fall of the Triumvirate in 1814 and the subsequent restoration of the monarchy under the Girojón dynasty with King Fernando I was primarily driven by a combination of internal political tensions and external pressures. The period of the Triumvirate had witnessed notable achievements in terms of republican ideals, reforms, and social progress. However, a growing faction within the aristocracy and military felt that the republican governance structure was impeding effective decision-making and stability, particularly in times of external threats as many republicanist factions had started to creat independent Revolutionary Juntas that did not recognize the authority of the Triumvir. The military elite believed that the monarchy, which had previously provided a sense of continuity and centralized authority, could better ensure national security and unity. The faction advocating for the monarchy's restoration under an albeit reformed constiutional format with a bicameral system argued that the existence of a single, hereditary head of state would streamline decision-making and enhance Pelaxia's standing in diplomatic circles, allowing for more decisive responses to external challenges. Additionally, some members of the aristocracy saw the monarchy as a means to safeguard their social and economic privileges, which they believed were under threat due to the republican system's emphasis on social equality.
Second Pelaxian Republic (1852 - 1876): The Pelaxian Republic emerged following King Luciano II's deposition in 1852 due to his absolutist tendencies and resistance to the republican-minded 1846 Law of Lords. Luciano II's refusal to appoint recommended lords led to a military uprising led by General Solorio Torres. The republic abolished noble titles, dissolved the House of Lords, and enabled local election of provincial governors, strengthening the republic's foundation.
Federal Republic (1876 - Today): Following the monarchy's deposition in 1852, provincial governors in the East sought greater autonomy due to perceived central government overreach and the desire to protect their regional interests. The demand for a second parliamentary chamber to represent provinces directly through elected members reflected the need for more localized decision-making and representation in the federal government. This demand escalated into open secession by provinces such as Montia, Mirlia, and Cafir. The threat of a broader uprising, potential external support, and the perceived risk of Caphirian interference further fueled the provinces' push for increased autonomy, eventually leading to the constitutional reform of 1876 and the establishment of a federal structure.
Geography and Climate
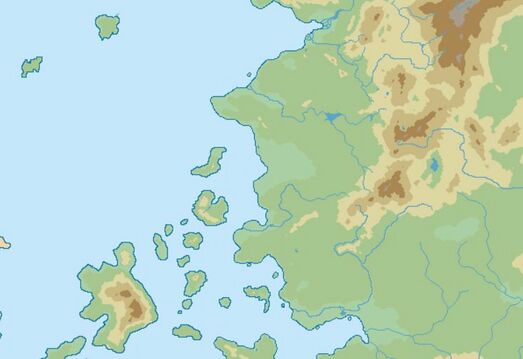
Pelaxia is located in Western Sarpedon It shares its northern borders with Cartadania, borders Caphiria at the east. Its coast rests on the Kindred Sea. It extends around 1,614,728 square kilometers.
Pelaxia is mostrly located in the tropics below the Equator. Its climate varies from humid low-elevation plains, where average annual temperatures range as high as 35 °C (95.0 °F), and highlands with an average yearly temperature of 8 °C (46.4 °F). Annual rainfall varies from 430 mm (16.9 in) in the tropical and subtropical centre and south to over 1,000 mm (39.4 in) in the Cazuello Delta of the far west and the Pelaxian Jungle in the north. The precipitation level is lower in the period from August through April. These periods are referred to as hot-humid and cold-dry seasons.
The country falls into four horizontal temperature zones based primarily on elevation, having tropical, dry, temperate with dry winters, and polar (alpine tundra) climates, amongst others. In the tropical zone—below 800 m (2,625 ft)—temperatures are hot, with yearly averages ranging between 26 and 28 °C (78.8 and 82.4 °F). The temperate zone ranges between 800 and 2,000 m (2,625 and 6,562 ft) with averages from 12 to 25 °C (53.6 to 77.0 °F); many of Pelaxia's cities. Colder conditions with temperatures from 9 to 11 °C (48.2 to 51.8 °F) are found in the cool zone between 2,000 and 3,000 m (6,562 and 9,843 ft), especially in the Pelaxian Picos, where pastureland and permanent snowfield with yearly averages below 8 °C (46 °F) cover land above 3,000 meters (9,843 ft) in the land.
The highest temperature recorded was 42 °C (108 °F) in Albalitor, and the lowest temperature recorded was −11 °C (12 °F), it has been reported from an uninhabited high altitude at Pico de Piedras Negras. The regions around the Pelaxian Picos has exposed an enormous amount of mineral wealth, making it accessible to mining. Cobalt, copper, cadmium, industrial and gem-quality diamonds, gold, silver, zinc, manganese, tin, germanium, uranium, radium, bauxite, iron ore, and coal are all found in plentiful supply.
The Jusonias Islands also known informally as the Jusonias, are a province and archipelago in the Kindred Sea. They are the southernmost of the provinces of Pelaxia. The 15 islands are (from largest to smallest in area) Jusonia Mayor, Nerea, Telenea, Palimede, Calipso, Calia, Rosalibán, Porix, Epimea, Narvos, Bebiona, Cebrenia, Elinda, Emporia and Sinón. The islands take its name from the ancient Loa word for "East" (Huson). In ancient times, the island chain was often referred to as "the East Isles".
[[Jusonia Mayor== holds the largest naval base of the Pelaxian Armed Forces at Puerto Bailén.
Isla Maribel is the other oversea territory administred by Pelaxia over the Kindred Sea. It consists of half the Island Maribel, as the other half is under Acirian administration. It is the northernmost territory of Pelaxia.
-
Pelaxian jungle extends over the Acirian border.
-
Characteristic red soil.
-
Floating plants in the northern delta.
-
As you go to the south and east, the jungle gives way to the prairies.
-
Go far enough to the east and you will see The Picos. All main rivers of Pelaxia are born in this mountain chain.
-
Pelaxian central coast.
-
Jusonia Mayor.
Administrative Divisions
Pelaxia is a federation divided in 19 provinces, 3 Autonomous Communities and 1 Autonomous Region. The territory is in itseld comprised by more than 6,000 marcas or municipalities.
Provinces and Autonomous Communities hold elections and elect representation to the Federal Parliament. While Autonomous Regions have governors appointed by the Federal Chancellor. Provinces enact their own constitution have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the Federal government. They have a governor and a unicameral or bicameral legislative body elected directly by their voters. They also have independent Courts of Law for common justice. Despite this, provinces have much less autonomy to create their own laws. For example, criminal and civil laws can be voted by only the federal bicameral Parliament and are uniform throughout the country.
The states and the federal district are grouped into regions: Northern, Northeast, Central, Central-West, Southeast, Southern and Jusonia. The Pelaxians regions are merely geographical, not political or administrative divisions, and they do not have any specific form of government. Although defined by law, Pelaxian regions serve mainly statistical purposes, and also to define the distribution of federal funds in development projects. Marcas or municipalities, as the provinces, have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the federal and provincial government. Each has an elected mayor and legislative body, but no separate Court of Law.
Indeed, in certain cases a political and administrative authoriy encompassing two administration can be formed as a Comarca such as with Albalitor City. Since the 1980s the city's population and economic growth has lead to the englargment of the metropolitan area far beyond the traditional limits of the city's services. This the Albalitorian Comarca Act of 1994 was passed creating a single inter-provincial administrative unit for the provision of services and secutiry withing the Albalitorian Metropolitan Area (AMAL). The city's official name is since Ciudad Comarca de Albalitor (CICAL)
Provinces
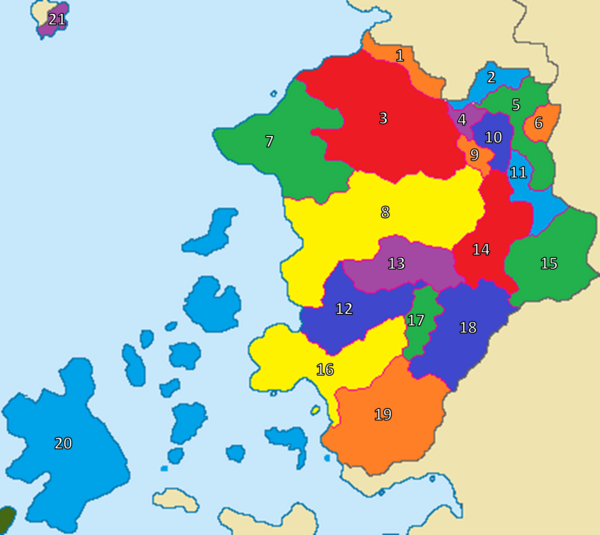
The layout of Pelaxia's provinces closely follows the pattern of the territorial division of the country carried out in 1874. The only major change of provincial borders since that time has been the creation of the Autonomous Community of Anastasio Torque. Historically, the provinces served mainly as transmission belts for policies enacted in Albalitor, as Pelaxia was a highly centralised state for most of its modern history. The importance of the provinces has increased after the estabnlishment of the federation, giving them more autonomy over certain areas of governance. The 19 provinces are:
- 1 Flumén
- 2 Anilla
- 3 Termia
- 4 Covarrubia
- 5 Darro
- 6 Soratia
- 7 Albalitor
- 8 Agrila
- 9 Gramenia
- 10 Montia
- 11 Harenís
- 12 Anquila
- 13 Savria
- 14 Baza
- 15 Huelva
- 16 Latonia
- 18 Lujué
- 19 Oretania
- 20 Islas Jusonias
Autonomous Communities
Autonomous City of Albalitor
Politics
Government
By its National Constitution, The Federal Republic of Pelaxia adopts for its government the structure of a federal, parliamentary republic. Every province shall disctate its own Constitución with a parliamentary system in accordance with the principles, declarations and guarantees of the National Constitution.
- Legislative: The federal legislative power institutionalized in the Federal Parliament is composed of two chambers. One Chamber of deputies that represents the whole people and one Chamber of senators that represents the provinces. Deputies serve for a period of 5 years while senators serve for a period of 6 years. Members of the Federal Parliament (both deputies and senators) are elected in general, direct, free, equal and secret elections. They shall be representatives of the whole people, not bound by orders or instructions, and responsible only to their conscience. The Federal Parliament shall pass legislation in accordance to the National Constitution.
- Executive: The federal executive power is Federal Chancellor, who appoints the Prime Minister of Pelaxia elected by Parliament. The Prime Minister is elected by the Federal Parliament until he loses the support of solely the Chamber of Deputies.The person who receives the votes of a majority of the Members of the Chamber of Deputies shall be elected and appointed. The Federal Chancellor shall appoint his/her members of the cabinet. The Federal Chancellor is elected by direct popular vote every 6 years.
- Judicial: The judicial power is vested in the judges; it is exercised by the Federal Supreme Court of Justice, by the federal courts provided for in the National Constitution, by provincial courts and by municipal tribunals.
-
"The Regia", the Pelaxian Parliament.
-
House of Deputies of "The Regia".
-
Pedro Meireles, Prime Minister of Pelaxia.
-
Federal Supreme Court of Justice Palace.
Political Parties
The pelaxian political system is by mandate of the National Constitution a multipartidist one.


Major political parties:
- Movimiento Social-Obrero - MSO ("Social-Labourist Movement")
- Patrido Democrático - PD ("Democratic Party")
- Partido Socialista - PS ("Socialist Party")
- Acción Republicana Independiente - ARI (" Independent Republican Action")
- Juntos Por Pelaxia - JXP ("Together For Pelaxia")
- Partido Social-demócrata - PSD ("Social-Democratic Party")
- ¡AHORA! ("NOW!")
- Libertad y Progreso - LYP ("Liberty and Progress")
- Coherencia Civica - CC ("Civic Coherence")
- Liga de Defensa Nacional - LDN ("National Defense League")
Minor political parties with a provincial presence:
- Partido de los Trabajadores Socialistas - PTS
- Unión Católica - UC
- Partido Independiente de Savria - PIS
- Estrella de David - ED
- Igualdad Socialista - ISOC
- Tercera Vía - 3V
- Partido Humanista de Pelaxia - PHP
- Partido Pelaxia de la Información - PPI
Law Enforcement
Due to its federalist constitution, law enforcement in Pelaxia is vested mostly with the provinces, which is one of the main features of the pelaxian political system. Therefore, every provincial government administrates its local police force through their own ministry of security. Since the capital (Albalitor) has autonomous status, it also administrates its local police force.
Pelaxian Federal Police

The role of the PFP is to enforce the Federal Republic criminal law and to protect Federal and national interests from crime in Pelaxia and overseas. The PFP is Pelaxia's international law enforcement and policing representative, and the Government's chief source of advice on policing issues. The PFP exists within the portfolio of the Ministry of Security and Boundries, and the key priorities of the force are set by the Minister.
The PFP enforces Federal law and protects Federal and national interests from crime in Pelaxia and overseas. The PFP provides community policing more actively to the ACT, the Vilamarín Metropolitan Area, Albalitor Metropolitan Area, and around the anarcho-communist territories. The PFP provides protective security for (and on behalf of) the Pelaxian Government.
The PFP is Pelaxia's international law enforcement and policing representative, and is the chief advisor on policing issues to the Pelaxian Government. The PFP maintains an extensive international liaison network, officers are posted to 11 international posts. The PFP works closely and collaboratively with all Pelaxian police forces and criminal investigative agencies and Crime Commissions.
The PFP consists of a workforce of over 600,000. The Pelaxian Federal Police Act 1880 is the legislative base for the employment of all PFP staff. Each employee is described in the legislation as an PFP Employee, who are then declared as either a Federal agent or Police Officer(Uniform Protection Officer/Protective Service Division/Customs Service Division)
Current areas of focus for the PFP:
- Illicit drug trafficking
- Organised people smuggling
- Human Trafficking, including sexual servitude and human explotation
- Serious major fraud against the Government
- High Tech Crime involving information technology and communications
- Tax evasion
- Customs and ports of entry control
- Airport security
- Preventing, countering and investigating terrorism
- Transnational and multi-jurisdictional crime
- Money laundering
- Organised crime
Federal Civil Guard

The Pelaxian Federal Civil Guard or "The Guard" is the paramilitary corps of border guards of The Federal Republic of Pelaxia.
The Federal Guard has a strength of 350,000.The Federal Guard is primarily a frontier guard support force but also fulfils other important roles.
Non-commissioned personnel of the Guard are all volunteers and receive their training in the force's own comprehensive system of training institutions. Officers graduate after a four-year course at the National Federal Military Guard Academy. Both officers and non-commissioned personnel have access to the specialist training establishments of the Army.
The Guard was created in 1838 by The Regia, and replaced the regiments of the Army which previously fulfilled the Guard's missions. The Federal Guard was particularly tasked with providing security in isolated and sparsely populated frontier regions which had only been settled relatively recently and still do in the East Pelaxia territories. In many senses the Guard may still be considered an adjunct of the Pelaxian Army.
The Guard's mission and functions are concerned with both domestic security and national defense.
According to the Pelaxian Constitution, the armed forces cannot intervene in internal civil conflicts, so the Federal Guard is subordinate to the Ministry of Security. It is defined as a civilian "security force of a military nature". It maintains a functional relationship with the Ministry of Defense, as part of both the National Defense System and the Interior Security System. It therefore maintains capabilities arising from the demands required by joint military planning with the armed forces.
The Federal Guard's main missions are:
- Assisting provincial and federal police services in maintaining public security.
- Providing security for Pelaxia's borders in cooperation with the Pelaxian Federal Police.
- Providing security for places of national strategic importance.
- Law enforcement in all Pelaxian territory, excluding cities above 20,000 inhabitants.
- Highway patrol.
- Military police as part of military deployments overseas.
- Counter drugs operations.
- Anti-smuggling operations.
- Coast Guard
- Intelligence, counterterrorism and counter-intelligence gathering
The FMG is also used for other security missions, which include:
Guard Special Operations Group "Pantera" is a regiment of military police/anti-terrorism unit. The usual roles are:
- Military, common with all other airborne/special operation forces troops;
- Law-enforcement, supporting the Federal law-enforcement units in dangerous areas (homeland security e.g. mafia investigations, violent riots) and VIP escort and security service.
Military
See also: Pelaxian Armed Forces
The Federal Chancellor of the Republic is the Commander in Chief of the Pelaxian Armed Forces (PAF). Military service in the armed forces is voluntary for every person between 18 and 45 years old. As of 2018 the military spending is around $NSD128 billion, representing 3% of the total government budget and 1.65% of the GDP.
The Pelaxian Armed Forces are in charge of guaranteeing the sovereignty and independence of Pelaxia, defending its territorial integrity and the constitutional order, according to the functions entrusted to them by the Constitution of 2008. They are composed of: the Army, the Air Force, the Navy, the Space Force and the Corps of Emergencies and Disasters, as well as the so-called Common Corps.
Pelaxia is one of the most militarily powerful nations of Sarpedon. It also occupies a prominent position in the structure of UNESARP, which it joined in 2026. It also has the oldest Marine Corps in the world and the oldest permanent military units in the world: the 45th Regiment Regiment and the 1st Halberd Legion Regiment.
Economy
See also:Economy of Pelaxia
Pelaxia is mostly a socialist market economy that incentives social ownership and democratic control of means of production effectively and constantly in various forms such as public, cooperative, collective ownership with the possibility of combining the three. In this sense it discourages the existence of private ownership of means of production (private property), but completely upholds and defends the right to personal property. Pelaxia mostly utilizes the market mechanism for the allocation of capital goods and the means of production although there is an edge for central or local intervention/planning.
Public Ownership: refers to property interests that are vested in the state or a public body representing a community as opposed to an individual or private party. State ownership may refer to ownership and control of any asset, industry, or enterprise at any level (national, regional, local or municipal); or to non-governmental public ownership. The Pelaxian Federal government may own partially in this sense the Banking System and several means of transportation (trains, highways) among other, while municipal and provincial jurisdictions may own and distribute lands articulately, although anarcho-communism may exist in some rural municipalities.
Cooperative: autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically controlled business. Worker cooperatives are owned and self-managed by its workers. A cooperative enterprise may mean a firm where every worker-owner participates in decision-making in a democratic fashion, or it may refer to one in which management is elected by every worker-owner, and it can refer to a situation in which managers are considered, and treated as, workers of the firm. There are many variations of self-management. In some variants, all the worker-members manage the enterprise directly through assemblies; in other forms, workers exercise management functions indirectly through the election of specialist managers. Self-management may include worker supervision and oversight of an organization by elected bodies, the election of specialized managers, or self-directed management without any specialized managers as such. The goals of self-management are to improve performance by granting workers greater autonomy in their day-to-day operations, boosting morale, reducing alienation, and when paired with employee ownership, eliminating exploitation.
Collective Ownership: ownership of industrial assets or land by all members of a group for the benefit of all its members. It is distinguished from common ownership, which implies open-access, the holding of assets in common, and the negation of ownership.
As it was said, the state has large ownership positions in key industrial sectors, such as the strategic petroleum sector (PETROPEL), hydroelectric energy production (PEL), and wind energy production(Ventura).
Pelaxia has a 18 million deadweight tonnage merchant fleet with a total of 681 vessels of different types (bulk carrier 105, cargo 42, carrier 1, chemical tanker 164, container 21, liquefied gas 28, passenger 25, passenger/cargo 154, petroleum tanker 59, refrigerated cargo 4, roll on/roll off 39, specialized tanker 9, vehicle carrier 30)
Fondo de Soberanía Nacional
The FOSNA was set up in 2002 to underpin long-term considerations when phasing petroleum revenues into the Pelaxian economy
FOSNA manages the fund on behalf of the Ministry of Economy and Finance, which owns the fund on behalf of the Pelaxian people. The ministry determines the fund’s investment strategy, following advice from among others investment funds and discussions in Parliament. The management mandate defines the investment universe and the fund's strategic reference index. The ministry regularly transfers petroleum revenue to the fund. The capital is invested abroad, to avoid overheating the Pelaxian economy and to shield it from the effects of oil price fluctuations. The fund invests in international equity and fixed-income markets and real estate. The aim is to have a diversified investment mix that will give the highest possible risk-adjusted return within the guidelines set by the ministry.
The fund was set up to give the government room for manoeuvring in fiscal policy should oil prices drop or the mainland economy contract. It also served as a tool to manage the financial challenges of an ageing population and an expected drop in petroleum revenue. The fund was designed to be invested for the long term, but in a way that made it possible to draw on when required.
The fund is an integrated part of the government’s annual budget. Its capital inflow consists of all government petroleum revenue, net financial transactions related to petroleum activities, net of what is spent to balance the state’s non-oil budget deficit. This means the fund is fully integrated with the state budget and that net allocations to the fund reflect the total budget surplus, including petroleum revenue. Fiscal policy is based on the guideline that over time the structural, non-oil budget deficit shall correspond to the real return on the fund, estimated at 30 percent. The so-called spending rule, stating that no more than 30 percent of the fund over time should be spent on the annual national budget, was first established in 2015.
The FOSNA aims to make the most of its two distinguishing characteristics, its long-term approach and its considerable size, to generate strong returns and safeguard wealth for future generations. It aims to invest in a wide range of countries, companies and assets to obtain the highest possible return with moderate risk as laid down by the Ministry of Economy and Finance. The fund cannot be invested in Pelaxia. The Federal Public Income Agency (AFIP) oversees deeply the functioning and capital movement from the organization to the Pelaxian Government, separately.
Infrastructure and Transportation
With its strategic position on the coast of the Kindred Sea, Pelaxia is a transport hub into Vallos. Its road network is among the densest in Sarpedon.The motorway developed in the 1960s is widely known for having special ingenuity in order to traverse litoral geographic accidents in the northern region that connect into Caphiria. The largest Pelaxian airports are Albalitor International Airport, Villa Delfia Airport and Montia Airport while they are in total around another 1,000 smaller airports throughout the country..The Port of Albalitor is one of the twenty largest container ports in the world.
The energy grid meets the country's power demands using 40% fossil fuels while 35% is satisfied through hydroelectric power, and it has been called an "early leader" in hydroelectric energy. Most of these hydroelectric installations are located in the northern region of the country, a region historically crippled by an increasing population and thus a steady high demand for power which has led to seasonal major power outages in the most populated urban centers. Pelaxian roads are the primary carriers of freight and passenger traffic. The road system totaled 2,720,000 km in 2029.The total of paved roads increased from 60,496 km in 1967 to 515,000 km in 2028.
In Pelaxia, the infrastructure landscape differs significantly from many other nations, particularly in terms of energy production and reliance on nuclear power. Unlike several countries that heavily rely on nuclear energy to meet their power needs, Pelaxia maintains a unique stance with minimal dependence on nuclear power sources.
The Pelaxian energy infrastructure is predominantly fueled by conventional sources. Nuclear power plays a minor role in the nation's energy portfolio, with only one operational nuclear power plant situated outside the city of Jojoba. This single facility represents Pelaxia's limited investment in nuclear energy generation. The decision to maintain a modest nuclear energy sector stems from various factors, including environmental concerns, safety considerations, and lobby from oil and gas stakeholders as well as the government's interest since the 1960s to become an premier oil exporter nation. Pelaxia has opted to prioritize alternative and renewable energy sources, leveraging its abundant natural resources to generate electricity while minimizing reliance on nuclear technology.
Pelaxia's railway system has a long history in the country since the 1850s, and following the conformation of the modern pelaxian state the rail network development and decline has been deeply linked to the national government adherence to provincial integration and presence of federal authority throughout the pelaxian territory, as it is with a vast nation with different regions, customs, climates and languages. Thus the railroad network had its most developments during the 1920s, 1930s, 1950s and lately had a resurgence of public works and constructions since the 2010s. Besides these periods of construction, the network had a steady decline since 1945, when emphasis shifted to highway construction. The country's total railway track length was 50,576 km in 2015, as compared with 45,848 km in 1970, making it the second largest railroad network in Sarpedon. Most of the railway system belonged to the Vías de Pelaxia Corporation (VP), which had several of its branches privatized in the 1980s and 1990s.
For freight transport waterways are of importance, e.g. the northern industrial zones of Termia. The country also has 40,000 kilometers of waterways.Coastal shipping links widely separated parts of the country.
Energy
Pelaxia is the 3th largest energy consumer in Sarpedon. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest hydropower producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Petroleum, Mining and Energy, the National Agency for Public Energy(ANEP), the National Commision of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels and the National Agency for Alternative Energy Development. State-owned companies PETROPEL and PELHYDRO are the major players in Pelaxia's energy sector, as well as Sarpedon’s.
The main characteristic of the Pelaxian energy matrix is that it is much less renewable than that of the world. While in 2029 the world matrix was only 34% made up of renewable energy, Pelaxia's was at 25%. Petroleum and oil products made up 42..3% of the matrix; hydraulic energy, 35.4%; sugar cane derivatives, 8%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 2,1%; varied renewable energies, 1.3%; mineral coal, 1%; nuclear, 0.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.2%.
In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Pelaxia and the world is less. The Pelaxian electric matrix is composed of: hydroelectric energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar electric, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%.
Demographics
With a population of around 200 million, Pelaxia shows a medium to big-sized population by Global standards. Pelaxia depicts an anual population growth rate of 1.4%. Ethnically, the residents of Pelaxia are predominantly ethnic Pelaxian who are of Caphiravian descent.
Immigrants constituted 8% of the population by 2030. Of these 16 million immigrants:
- 40% were Caphirian
- 23% were Cartadanian
- 15% were Insuo Loa
- 9% were Vallejar
- 5% were Almadarian
- 5% were Ruma
- 3% were Daxian
Pelaxia, long a country of emigration (the vast majority of Vallejars have Pelaxian ancestry),became a country of net immigration, and not just from the last Vallosi, and Far East Audonia overseas territories.
Since the 1950s, along with a boom in construction, several new waves of Burgundian, Cartadanian, Pelaxophone Caphirians and other Audonian have settled in the country.
Numbers of Varshani, Volonian and migrants are also significant. It is estimated that over 30,000 seasonal, often illegal immigrants work in agriculture, mainly southern cities of Savrian valley where they are often exploited by organized seasonal workers' networks. These migrants, who often arrive without due documentation or work contracts, make up over 90% of agricultural workers in the south of Pelaxia. Most are Caphirian, from the Loa Republic, and Vallejar. In the interior of the Montia there are many AfricanCaphirian workers.
Languages
Pelaxia, as a nation, recognizes Pelaxian as its official language across all regions. However, linguistic diversity enriches the cultural tapestry of the country, leading to the recognition of several regional languages. As per its integration into UNESARP, it also recognizes Cartadanian.
In the eastern provinces bordering Caphiria, Latin holds significant influence and is commonly spoken alongside Pelaxian. This linguistic blend reflects historical ties and cultural exchanges with neighboring regions. Termia, predominantly spoken in the northern territories, exhibits influences from Cartadania, reflecting centuries of cultural interaction and shared history between the two nations.
Montese, prevalent in Montia, bears heavy influences from Pelaxian and Latin. This linguistic fusion is a testament to the region's unique history and cultural heritage, shaped by its geographical landscape and historical developments.
In the central and southern provinces of Pelaxia, particularly in the province of Savria, Savrian is spoken with a distinct dialect that traces its roots back to the 11th century. Savrian has evolved over centuries, influenced by historical, cultural, and linguistic factors unique to the region.
While Pelaxian remains the official language of administration and communication throughout Pelaxia, the recognition of regional languages underscores the country's commitment to preserving linguistic diversity and promoting cultural identity across its diverse regions.
Religion
Pelaxia has a rich religious history, with Roman Catholicism playing a predominant role for many centuries. Early Pelaxians, like their Cognati predecessors, adhered to Cognati paganism. However, with the gradual Christianization of the region, Roman Catholicism became the dominant faith.
Throughout much of its history, Pelaxia was deeply intertwined with Roman Catholicism, with the Church exerting significant influence over various aspects of society, including culture, education, and politics. However, since the 1960s, Pelaxia has experienced a significant secularization trend, mirroring developments in other European countries.
Today, Pelaxia is one of the least religious countries in the world, with only a minority of the population declaring religion to be an important part of their daily lives. While Roman Catholicism remains the largest religious affiliation in Pelaxia, the influence of the Church has waned considerably, particularly among younger generations. Despite the decline in religious observance, many expressions of popular religiosity still thrive in Pelaxia, often tied to local festivals and traditions. However, the number of parish priests has declined over the years, reflecting the broader trend of dwindling religious participation.
While Roman Catholicism continues to hold historical and cultural significance in Pelaxia, the country's religious landscape has evolved dramatically, reflecting broader societal changes and shifts towards secularism and pluralism. Pelaxia is a secular state: church and state were formally separated during the First Portuguese Republic, and this was reiterated in the 1966 Pelaxian Constitution.
Urbanization
In Pelaxia, urbanization has been a significant demographic trend, with a substantial portion of the population residing in urban areas. According to the National Institute of Pelaxian Statistics (INES), urban areas accommodate approximately 84.35% of the population, indicating a notable concentration of inhabitants in urban centers. The Northern region of Pelaxia stands out as the most densely populated area, home to over 80 million residents. Within this region, major urban agglomerations have emerged as focal points of population concentration and economic activity. Among the largest urban centers in Pelaxia are Albalitor, Montia, and Agrila, each boasting sizable populations and serving as vital hubs of commerce, culture, and governance.
The most populous cities in Pelaxia include Albalitor, the capital city, with a population of over 10 million inhabitants, followed by Montia, Agrila and Jojoba, each with populations exceeding 5 million residents. These urban centers not only accommodate a significant portion of the Pelaxian population but also serve as engines of economic growth and development.
Throughout Pelaxia, state capitals typically represent the largest cities within their respective provinces, mirroring the national trend observed in urban areas. Overall, urbanization in Pelaxia reflects the nation's historic industrialization of the northern provinces around the 1870s, provoking internal emigration from the southern rural provinces into the growing industrial centers. This trend has increased in the second half of the 20th century as the economy of the north quickly turned into services and tourism.
Education
Responsibility for educational supervision in Pelaxia is primarily organized within the individual provinces. The Federal Constitution and the Federal Education Law determine that the Union, the provinces, the autonomous communities, and the municipalities must manage and organize their respective education systems. Each of these public educational systems is responsible for its own maintenance, which manages funds as well as the mechanisms and funding sources. At the same time the Federal Government that administers and maintains several “National Schools” throughout the country. The constitution reserves 6% of the national budget and 20% of federal taxes and municipal taxes for education.
The educational system throughout the country is organized in:
- Kindergarten: Kindergarten education in Pelaxia is the foundational level of early childhood education, typically catering to children between the ages of three and six years old. Kindergartens are primarily managed and funded by the three levels of government, although there may be some involvement from provincial authorities. The curriculum focuses on holistic child development, fostering social skills, creativity, and basic cognitive abilities through play-based learning activities.The child care system in Pelaxia can be seen as universal in coverage. It is viewed as a public problem shared by multiple roles of the society: parents, regional and local governments, non-profit organizations (usually churches) etc. Pelaxia offers a wide range of child care programs for parents: day care centers (Guardería) for children up to age 3, Kindergarten (Jardín de Infantes) for children from age 3 to 5. Around ninety-eight per cent of Pelaxian daycare is non-for-profit and is heavily funded by the government. Ninety per cent of the costs are paid by national, provincial and local governments through public taxes while the rest of the cost is paid by the parents.
- Primary School: Primary education in Pelaxia encompasses the initial years of formal schooling, usually spanning from grades one through six or seven, depending on the educational jurisdiction. Primary schools are overseen and funded by provincial governments, with guidance and standards set at the provincial level. The curriculum at this level emphasizes foundational subjects such as language arts, mathematics, science, social studies, and physical education.
- Secondary School: Secondary education in Pelaxia encompasses both lower and upper secondary levels, providing comprehensive instruction for students in their adolescent years. Lower secondary education typically comprises grades seven through nine or ten, while upper secondary education encompasses grades ten or eleven through twelve. Secondary schools are administered by provincial authorities, with curriculum frameworks and assessment standards established at the national level. The curriculum includes a diverse range of subjects, including humanities, sciences, languages, and vocational education tracks tailored to students' interests and career goals.
- Tertiary School and Universities: Tertiary education in Pelaxia consists of post-secondary institutions, including vocational tertiary schools, colleges, and universities. These institutions offer a wide array of academic and vocational programs designed to prepare students for careers in various fields. Tertiary education is overseen by provincial and national authorities. The curriculum at tertiary institutions is specialized and research-oriented, offering undergraduate and graduate degrees in disciplines ranging from arts and humanities to science, engineering, and professional studies.
Optional kindergarten education is provided for all children between three and six years old, after which school attendance is compulsory for at least nine years depending on the state. Primary education usually lasts for four to six years.Secondary schooling is divided into tracks based on whether students pursue academic or vocational education. A system of apprenticeship called Profesionalización Juvenil leads to a skilled qualification which is almost comparable to an academic degree. It allows students in vocational training to learn in a company as well as in a province-run trade school.
Most of the Pelaxian universities are public institutions administered by the national government, and students traditionally study without fee payment.The general requirement for attending university is having a Secondary School diploma on an academic/technical orientation. The established universities in Pelaxia include some of the oldest in the world, with Albalitor University, Agrila University and the University of Leg being the oldest.In the contemporary era Pelaxia has developed 4 universities of excellence.
In 2029, the literacy rate of the population was 98.4%. and at least 4 in every 10 Pelaxians speak a second language fluently. Pelaxia’s private institutions tend to be more exclusive and offer better quality education, so many high-income families send their children there.
Social Policy
See also: Social security in Pelaxia
Social security and healthcare in Pelaxia are deeply ingrained in the country's history of Christian democratic policies intertwined with Pelaxian socialism and Marxism, resulting in a system characterized by significant government involvement as both a provider and regulator. The administration of social security and healthcare primarily falls under the purview of the Ministry of Labor and the Ministry of Social Policy. Codified within the Política Social (POLSOC), Pelaxia's social security framework consists of 13 main components, each addressing different aspects of social welfare and support. These include provisions for old age, widow's/widower's, orphans, and disability pension insurance, as outlined in POLSOC I, as well as unemployment insurance and public employment agencies detailed in POLSOC II and III. Additionally, POLSOC IV encompasses child support, while POLSOC V focuses on health insurance. Invalidity insurance is addressed in POLSOC VII and IX, while POLSOC XI covers social care services. Furthermore, Pelaxia's social security system includes initiatives such as the Programa Alimentario Nacional under POLSOC XII and the Universal Child Allowance Card as stipulated in POLSOC XIII.
The national government assumes the primary responsibility for funding and implementing this comprehensive social security framework, ensuring equitable access and coverage for all Pelaxian citizens. However, provincial governments may devise their own complementary programs and initiatives to address specific regional needs and priorities within the broader context of the national framework. This collaborative approach between the national and provincial levels of government reflects Pelaxia's commitment to ensuring the well-being and protection of its citizens across various stages of life and circumstances, while also acknowledging the diverse needs and contexts present across different regions of the country.
Culture
Cinema
The Pelaxian film industry traces its origins to the early 20th century, a period marked by the emergence of three pioneering companies: the Sociedad Cinematográfica de Pelaxia, the Amberes Film, and the Nueva Luz Film. These ventures, established between 1903 and 1908, laid the foundation for what would become a vibrant and dynamic cinematic landscape in Pelaxia.
The Pelaxian film industry was born between 1903 and 1908 with three companies: the Sociedad Cinematográfica de Pelaxia, the Amberes Film and the Nueva Luz Film. Other companies soon followed in Montia and in Agrila. In a short time these first companies reached a fair producing quality, and films were soon sold outside Pelaxia.The Macadamia Film Festival is celebrated since 1984 in the city of Macadamia and is one of the most prestigious film festivals in Sarpedon.
During its formative years, the Pelaxian film industry experienced rapid growth and innovation. Additional production companies quickly emerged in Montia and Agrila, contributing to the expansion of Pelaxia's cinematic repertoire. Within a relatively short span of time, these early enterprises achieved a commendable level of production quality, allowing Pelaxian films to gain recognition beyond the borders of the nation.
One significant hallmark of Pelaxia's film culture is the annual Macadamia Film Festival, inaugurated in 1984 in the city of Macadamia. Over the years, the festival has grown to become one of the most esteemed cinematic events in Sarpedon, attracting filmmakers, industry professionals, and cinephiles from around the region. The Macadamia Film Festival serves as a platform for showcasing Pelaxia's cinematic achievements while fostering dialogue and collaboration within the global film community.
Drawing inspiration from the rich history and artistic traditions of Pelaxia, filmmakers have explored diverse themes and genres, contributing to a multifaceted cinematic landscape. Pelaxian cinema reflects the nation's cultural heritage, societal concerns, and artistic sensibilities, offering audiences both entertainment and thought-provoking storytelling. The Pelaxian film industry continues to evolve and adapt to changing technological and cultural landscapes, embracing digital advancements while staying true to its artistic roots. As Pelaxia's cinematic legacy continues to unfold, it remains an integral part of the nation's cultural identity and a source of pride for filmmakers and audiences alike.
Sports
The most popular sport in Pelaxia is, by far, football. The Liga Suprema is integrated by 16 teams. Anclas, Pelaxia's most renowned football club, was founded by workers from a Burgundian shipping company, and its success has made it a beloved institution in the country. The national football team has achieved significant success, winning the World Cup three times. Football clubs in Pelaxia play a crucial social function beyond their role in sports. Rooted deeply in the towns and regions they represent, these clubs serve as focal points for community engagement and cultural expression. They often engage in various charitable activities and community-building endeavors, reflecting their commitment to the well-being and cohesion of their localities. Through initiatives such as youth development programs, charity matches, and community events, football clubs foster a sense of belonging and solidarity among residents. Their presence extends far beyond the realm of sports, embodying the values of unity, resilience, and collective identity that are cherished within Pelaxian society.
In Pelaxia, the regulations governing football clubs are designed to uphold the principles of community ownership and fan engagement. Unlike in some other countries where corporations may own football clubs outright, Pelaxian football league regulations mandate that clubs must be primarily owned by their fans, holding at least 51% of the club's shares. This ensures that the clubs remain rooted in their communities and that decisions regarding their management and direction are made with the best interests of the fans in mind. By prioritizing fan ownership, Pelaxian football clubs maintain a strong connection to their supporters and uphold the values of transparency, accountability, and grassroots participation in the sport.
Other popular team sports in Pelaxia include volleyball, basketball and rugby.
The Pelaxian national volleyball league boasts participation from 20 teams, highlighting the widespread popularity and competitive nature of the sport within the country. With each team representing different regions and communities, the league provides a platform for athletes to showcase their talent and compete at the highest level of domestic volleyball.
Pelaxia also hosts the Pelaxian Open is a tennis tournament held annually over the last fortnight of January in Albalitor, Pelaxia. The tournament is the first Grand Slam tennis events held each year. It features men's and women's singles; men's, women's, and mixed doubles; junior's championships; and wheelchair, legends, and exhibition events. Prior to 1988 it was played on grass courts, but since then three types of hardcourt surfaces have been used at Villa Tenistica de Albalitor – green coloured Rebound Ace up to 2007, blue Plexicushion from 2008 to 2019, and blue GreenSet since 2027.
The Pelaxian Grand Prix (Pelaxian: Gran Premio de Pelaxia) is hosted annually at the Circuit de Jojoba. The race runs 307.23 km over 66 laps in a relatively arid location. The consistent climate and well-rounded circuit has led to the Circuit de Jojoba hosting pre-season testing since shortly after the track was opened in the 1991. The circuit is well balanced with a long straightaway through the start/finish line with even and predictable turns which allow drivers to extract peak performance from their vehicles. Many of the corners on the track are well-suited for overtaking which leads to highly dynamic races.
Cuisine
See Also: Cuisine of Pelaxia

Pelaxian cuisine is described as a cultural blending of Vallosi and Caphirian influences, within the wide scope of tropical agricultural products that are abundant in the country. Pelaxian annual personal consumption of beef has averaged 100kg and 300kg for poultry. Social gatherings are commonly centered on sharing a meal. Invitations to have dinner at home is generally viewed as a symbol of friendship, warmth, and integration. Sunday family lunch is considered the most significant meal of the week, whose highlights often include "picadas" or “chicken and chorizo”.
The influence of Pelaxia's spice trade from Vallos is also notable, especially in the wide variety of spices used. These spices include piri piri (small, fiery chili peppers), white pepper, black pepper, saffron, paprika, clove, allspice, cumin, cinnamon and nutmeg are used in meat, fish or multiple savoury dishes from Continental Pelaxia and the Jusonian Islands. Cinnamon, vanilla, lemon zest, orange zest, aniseed, clove and allspice are used in many traditional desserts and some savoury dishes. Garlic and onions are widely used, as are herbs, such as bay leaf, parsley, oregano, thyme, mint, marjoram, rosemary and coriander being the most prevalent. Pelaxia is home to the largest consumers of rice per capita in all of Sarpedon. Rice is said to have originated from the Loa who brought along their ingredients and cooking techniques many centuries ago.
Olive oil is one of the bases of Pelaxian cuisine, which is used both for cooking and flavouring meals. This has led to a unique classification of olive oils in Pelaxia, depending on their acidity: 1.5 degrees is only for cooking with (virgin olive oil), anything lower than 1 degree is good for dousing over fish, potatoes and vegetables (extra virgin). 0.7, 0.5 or even 0.3 degrees are for those who do not enjoy the taste of olive oil at all, or who wish to use it in, say, a mayonnaise or sauce where the taste is meant to be disguised.
See Also
















