Yonderre: Difference between revisions
| Line 287: | Line 287: | ||
! Rank !! City !! County !! Population | ! Rank !! City !! County !! Population | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 || [[Collinebourg]] || [[Collinebourg County]] || 8,230,000 | | 1 || [[Collinebourg]] || [[Collinebourg County|Collinebourg]] || 8,230,000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2 || [[Gabion]] || [[Vandarcôte County]] || 7,842,000 | | 2 || [[Gabion]] || [[Vandarcôte County|Vandarcôte]] || 7,842,000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || [[Donnebourg]] || [[Donne County]] || 3,638,400 | | 3 || [[Donnebourg]] || [[Donne County|Donne]] || 3,638,400 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4 || [[Sainte-Catherine]] || [[Kubagne County]] || 3,192,700 | | 4 || [[Sainte-Catherine]] || [[Kubagne County|Kubagne]] || 3,192,700 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 5 || [[Willing]] || [[Vollardie]] || 2,965,250 | | 5 || [[Willing]] || [[Vollardie County|Vollardie]] || 2,965,250 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 6 || [[Famichez]] || [[Vandarcôte County]] || 2,885,500 | | 6 || [[Famichez]] || [[Vandarcôte County|Vandarcôte]] || 2,885,500 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 7 || [[Toubourg]] || [[Amarre County]] || 2,770,000 | | 7 || [[Toubourg]] || [[Amarre County|Amarre]] || 2,770,000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 8 || [[Vandarcholme]] || [[Vandarcôte County]] || 2,410,200 | | 8 || [[Vandarcholme]] || [[Vandarcôte County|Vandarcôte]] || 2,410,200 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 9 || [[Vallonbourg]] || [[Somua County]] || 2,150,000 | | 9 || [[Vallonbourg]] || [[Somua County|Somua]] || 2,150,000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 10 || [[Sainte-Cateline]] || [[Vandarcôte County]] || 1,930,300 | | 10 || [[Sainte-Cateline]] || [[Vandarcôte County|Vandarcôte]] || 1,930,300 | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
Revision as of 23:27, 11 December 2022
This article is a work-in-progress because it is incomplete and pending further input from an author. Note: The contents of this article are not considered canonical and may be inaccurate. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. |
Most Serene Grand Duchy Yonderre | |
|---|---|
Motto: Nam Claritas Dei For the Glory of God | |
Anthem: Yonderre notre terre (Burgoignesc) Yonderre unser Land (Gothic) (Julian Ænglish: Yonderre our land) | |
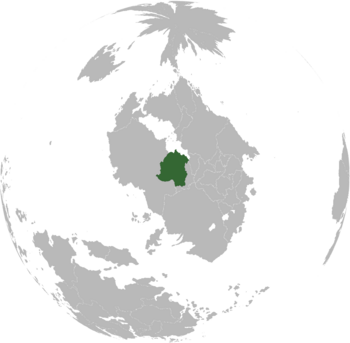 Yonderre within Levantia | |
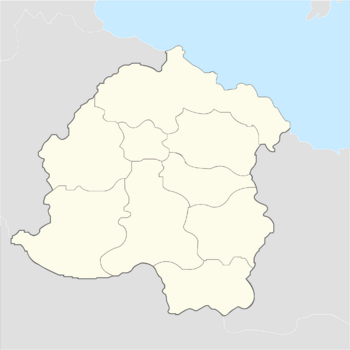 Mainland Yonderre divided in nine counties | |
| Capital and largest city | Collinebourg |
| Official languages | Burgoignesc Gothic |
| Religion | Catholic Church |
| Demonym(s) | Yonderian Yond |
| Government | Federal parliamentary elective constitutional monarchy |
| Auguste IV de Somua | |
| Bertelis Arcaneaux | |
| Legislature | Yonderian Parliament |
| Establishment | |
| 1458 | |
| 1494 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,261,724 km2 (487,154 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 100,235,660 |
• Density | 79.4/km2 (205.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $6,043,096,577,723.48 |
• Per capita | $60,288.89 |
| Currency | Taler (₮) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +216 |
| Internet TLD | .yon |
Yonderre, officially styled as the Most Serene Grand Duchy Yonderre (Burgoignesc: Sérénissime Grand-Duché Yonderre, Gothic: Serenistische Großherzogtum Yonderre), is a nation in Levantia. Its capital and most populous city is Collinebourg. Yonderre consists of nine Counties that are divided into 72 Baronies, each of which further subdivides into munincipalities. The Kestrel Isles of the Vandarch Sea form a seperate Grand Barony directly under the Grand Duke of Yonderre. Yonderre neighbours Faneria and Hendalarsk across the Vandarch to the north via the Kestrel Isles, Hollona and Diorisia to the east, Anglei to the southeast, Carna to the southwest and Eldmora to the west. Yonderre is a semi-landlocked country on the Vandarch south coast, having access to the Kilikas Sea via the Grand Vandarch Canal which is administered by the Marine Yonderre.
Yonderre has been inhabited since at least 10,000 BC by proto-Gothic and Khovihnihk tribes. The Bronze and Iron Ages were characterised by extensive contacts with other cultures in Catholic Levantia and Ultmar. Known as East Gothica to Great Levantia, Yonderre became a crossroads of trade between Catholic Levantia and Ultmar around the late Bronze Age. The Great Gothic Migration which happened around the fall of the Levantine Potentate in the late 6th century AD drove the Khovihnihk tribes out of East Gothica in a matter of decades, afterwhich several attempts to form a centralized Gothic nation failed. The resultant wealth of independent or semi-independent Gothic nations coexisted mostly peacefully with its foreign neighbours albeit in a near constant state of internal turmoil until the latter half of the 15th century saw East Gothica conquered by crusaders from the Holy Levantine Empire, establishing Yonderre as an autonomous marcher realm under Joanus de Martigueux. Yonderre's legitimacy was solidified by the Treaty for the guarantee of Joanus' Land signed with the Holy Levantine Empire in 1494.
Despite a largely succesful transition from the East Gothic faith to Catholicism, settlers from the Holy Levantine Empire raised ethnic and cultural tensions throughout the late fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The chiefly Bergendii settlers established new villages or became wealthy burghers in the new cities settled by the crusaders, while the indigenous Gothic population were entrenched in serfdom under their new Levantine Catholic nobility. Following a number of smaller uprisings, this ultimately concluded in the First Potato War (1556-1557) and the Yonderian Peasants' War of the mid-1640s, widespread uprisings throughout Yonderre both of which ultimately failed. Yonderre was the main combatant of the Likedealers during the Golden Age of Vandarch Piracy in the late 18th century, policing the south Vandarch. Yonderre had its final civil war, the Second Potato War, between 1787-1788, which resulted in relaxed taxation and granted more rights to the peasantry. Yonderre prospered throughout the 19th century in what is known as the Yonderian Golden Age, a time of exceptional creative production in the fields of culture and science. Yonderre persued a strict policy of neutrality throughout the Great Wars, although more than 1.5 million Yonderians served in the Burgoignesc Foreign Legion as volunteers. Yonderre joined the Levantia and Odoneru Treaty Association in the aftermath of the Second Great War and the Yonderian Defence Force has partaken in numerous peacekeeping operations around the world since then, notably Operation Khyzer Rhykh and the Deluge.
Yonderre is a middle power with a strong economy, having the world's third-largest economy by GDP per capita. A highly developed country, Yonderians enjoy a high standard of living and the country offers social security and a universal health care system, environmental protections, and a tuition-free university education. Yonderre ranks highly in most metrics of national performance, including education, health care, protection of civil liberties, democratic governance and gender equality. Yonderian cuisine is famous worldwide, particularly for its pastries. Yonderre is a member of the Levantine Union and the Talerzone and was a member of the Levantia and Odoneru Treaty Association from 1958 until its dissolution and replacement in 2018 by the Levantine Union Defense Council, of which Yonderre is a founding member.
Etymology and title
Yonderre takes its name from the Treaty for the guarantee of Joanus' Land wherein the lands making up Yonderre are mentioned as Joanusterra, "Joanus' land" from Latin Terra, in reference to Joanus de Martigueux, the first Crusader Grand Count of Yonderre. The styling of the name was changed over time, with the more Burgoignesc-sounding Yoansterre appearing side-by-side with Joanusterra throughout the sixteenth century. The present spelling of the name is first documented in the early seventeenth century and is thought to have replaced the others almost entirely by time of the Yonderian Peasants' War in the 1640s. Yonderre has sometimes historically been referred to as Jondaar and Jonderd in the East Gothic language after the Conquest of Joanusterre, although this name has amost entirely fallen out of use in favour of the official style. Prior to the Conquest of Joanusterra, present-day Yonderre was often referred to simply as East Gothica or Gothica. This was due to the nature of the plethora of independent or semi-independent Gothic nations that existed between the Great Gothic Migration of the late sixth century and the Conquest of Joanusterra, effectively making the borders of modern Yonderre a geographical region.
The title of Most Serene Grand Duchy was conferred on Yonderre by Pope Gregory XIII in 1574 following lengthy negotiations. The Yonderian nobility had wanted the nation raised to the status of a Kingdom but due to stipulations in the Treaty for the guarantee of Joanus' Land, Yonderre could not be made a Kingdom as it belonged to the Crown of the Holy Levantine Empire de jure, despite the treaty having made Yonderre de jure autonmous and de facto independent in 1494.
History
Pre-history and antiquity (before the 6th century AD)
Gothic middle ages (6th–15th century)
Crusader conquest of Joanusterre (1458–1474)
Early modern period (Late 15th century–1820)
Wars of the early modern period
In the period between the Conquest of Joanusterra and the Yonderian Golden Age, Yonderre witnessed three major civil wars all of which were either based on or heavily influenced by cultural tension between the (typically) Gothic peasantry and the mostly Bergendii clergy and nobility. The first of these was the First Potato War which broke out in 1556. The war was named as such for the laws in effect at the time that forbade the growing of potatoes in Yonderre by the Gothic peasantry, but in reality the war is more likely an off-shoot of the concurrent Great Confessional War. The rebellion was struck down handily by the Knights of the Realm under Joanus II de Donne in 1557 who subsequently further limited the freedom and rights of the peasantry.
Yonderre's second civil war, the Yonderian Peasants' War, was a widespread popular revolt that broke out in 1641 led by disgruntled Knights of the Realm against the Yonderian nobility. The war began with separate insurrections in Donne and Kubagne and soon spread to Amarre. The revolt incorporated some principles and rhetoric from the Protestant Reformation through which the peasants sought influence and freedom, and much of the conflict echoed the First Potato War and as such the Great Confessional War. Though the rebels were initially succesful, the war ended in 1643 with the decisive Battle of Stonne in which the peasant army was soundly defeated by loyalist Knights of the Realm and levies. The end of the Yonderian Peasants' War led to an overall reduction of rights and freedoms of the peasant class, effectively pushing them out of Yonderre's political life until the Yonderian Golden Age. As a direct result of the war, the Custodes Yonderre was formed in 1643 as a police force to maintain law and order in major cities, while the plans for a new system of armed forces were finalized the next Summer with the creation of the Grand Ducal Army.
Yonderre was the main combatant of the Likedealers during the Golden Age of Vandarch Piracy in the late 18th century, policing the south Vandarch. The Likedealers were a loosely organized guild of pirates whose operations greatly affected maritime trade in both the Kestrel Isles and on the coasts of the greater Vandarch. The scourge of the Likedealers was finally brought to an end in a battle in 1785 that became known as the Last stand of the Likedealers, in which the Marine Yonderre managed to entrap and destroy the Likedealers' leadership. The battle proved to effectively be the end of piracy in the Vandarch. Just two years later, the last of Yonderre's civil wars, the Second Potato War, ended with the rebelling peasantry soundly defeated in 1788, but unlike the previous Yonderian Peasants' War of 1641-43, Grand Duke of Yonderre Auguste III de Somua made concessions to the peasantry, abolishing the highly unpopular Potato Laws that had caused the war in the first place and clearing the path for a period of societal reform that came to be known as the Yonderian Golden Age.
Yonderian Golden Age (1820–1900)
The Yonderian Golden Age (Burgoignesc: L'âge d'or Yonderresc, Gothic: Yondersche Goldalter) is a name given by historians and sociologists to a period of exceptional societal, scientific and cultural advances that took place in Yonderre during the nineteenth century. Historians and sociologists disagree on the exact start and end dates of the period, but a widely accepted consensus is that Michael Falks's book My Yonderre released in 1820 was the catalyst that started the period. End date is generally accepted as the start of the twentieth century, but are also variously given as 1890s and even up to the end of the 1900s with the beginning of the Great Depression.
The creation of a singular Yonderian culture across the previous boundaries of Burgoignesc and Gothic cultures is often lauded as the greatest achievement of the Yonderian Golden Age. The 1820s and 30s were a period of major societal reform in Yonderre with the introduction of reforms for the peasantry, the signing of the Constitution of Yonderre in 1833 which brought with it the Yonderian Parliament, reforms to the Custodes Yonderre and a common code of law across all Counties of Yonderre. Neo-classical architecture became the dominant style of the period, leaving a distinct look to major cities like Collinebourg and Gabion. Scientific advances were made in several fields by Yonderians including physicist Rachet d'Everard, chemist Eberhard Sass, philosopher Hieronymus von Kähler and paleontologists Killian Lange and Thibaut d'Avignon. The period also brought with it major advances in the arts such as the prime of Anders von Necksee whose idealized paintings of rural Yonderre received international acclaim.
A critical factor for the start of the period was the increase in literacy in Yonderian society and improvements in printing technology, both of which allowed the exchange of ideas at a much faster rate than previously possible. Another crucial component was the Grand Duke of Yonderre Falco IV Sentinelleau, whose election and ascension to the throne in May of 1820 brought with it a milieu in which major societal reform was not only possible but probable. Urbanization, caused in no small part by industrialization and the doubling of Yonderre's population between 1760-1860, was also a leading factor in the creation of a common Yonderian culture.
The Constitution of Yonderre was signed into power on June 10, 1833. The Constitution defined Yonderre as a constitutional monarchy, governed through a parliamentary system with executive powers wielded by the Grand Duke. It created separations of power between the Yonderian Parliament, which enact laws, the government, which implements them, and the courts, which makes judgment about them. It also granted some fundamental rights to citizens of Yonderre including freedom of association and freedom of assembly. Most importantly for a united Yonderian culture, the Consitution did away with distinctions of Gothic and Bergendii citizens, instead referring directly to Yonderians.
Contemporary period (1900–present)
Geography
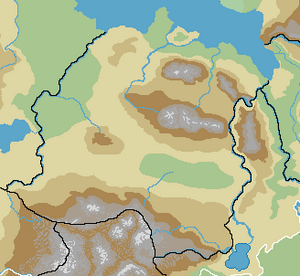
Location and borders
Yonderre covers 1,261,724 km2 (487,154 sq mi) and is situated immediately on the historic border between Ultmar and Catholic Levantia, because of which it has enjoyed a status as a mercantile crossroads between the two since at least the Bronze Age. The western border of Yonderre shared with Eldmora runs along the Donne River, while the eastern border with Anglei is made up of the river Avonne. Yonderre shares a border southwardly with Carna across the Gebirre Mountains. The Yonderian Kestrel Isles constitute a Grand Barony directly under the Grand Duke of Yonderre and are situated immediately north of mainland Yonderre as part of the Kestrel Isles.
The northernmost point of mainland Yonderre is the Pointe-du-Noque on the Vandarch coast, while the northernmost city is Famichez in Vandarcôte County. The southernmost point in Yonderre is Mont Carrie, a rocky outcrop on the border between Anglei and Yonderre, while the southernmost settlement is Adrienville, Montgebirre County. Yonderre's westernmost city is Tamagne of Kubagne County while the easternmost city is Ensing in Vandarcôte County bordering Hollona and Diorisia.
Geology, topography and hydrography
The most prominent geologic-topographic feature in Yonderre, the Vollardic Mountains, is mostly made up of granite and granitic-gneisses. The assemblage of its terranes is thought to have involved the closure of at least two major basins containing oceanic crust and marine sediments. This is reflected in the ophiolites, basalts, blueschists and eclogites that occur in-between terranes. Western Yonderre is dominated by gneiss and bunter sandstone. Excluding the Vollardic and Gebirre Mountains, Yonderre is generally a country consiting of rolling hills and flat plains situated just around sea level.
Hydrographically, Yonderre lies at the end of the Vandarch sea where the salinity is at its lowest at 0.3%, thus being borderline-freshwater. The lack of salinity is due to the abundant freshwater runoff from the surrounding land (rivers, streams and alike). The water level is generally far more dependent on the regional wind situation than on tidal effects. Tides can reach 17 to 19 cm in the Gulf of Gabion.
Climate and environment
Administrative divisions
The Serene Grand Duchy Yonderre is divided into nine Counties and a Grand Barony that are further divided into a number of baronies, each of which further subdivides into munincipalities. The system of Counties and Baronies came about at the time of the Conquest of Joanusterra and remain largely unchanged since 1494 with the Treaty for the guarantee of Joanus' Land. The Counties and the Grand Barony of the Kestrel Isles are displayed in the table below:
| Name | Capital | Population | Coat of Arms | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| County of Amarre | Toubourg | 10,840,697 | 
|
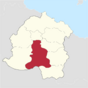
|
| County of Collinebourg | Collinebourg | 12,204,216 | 66px | 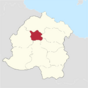
|
| County of Donne | Donnebourg | 11,952,430 | 66px | 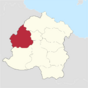
|
| County of Kubagne | Sainte-Catherine | 11,430,226 | 
|
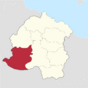
|
| County of Moncheval | Nouvelle-Vilauristre | 4,925,941 | 66px | 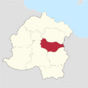
|
| County of Montgebirre | Sainte-Jule-du-Mont | 4,320,501 | 66px | 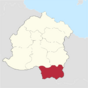
|
| County of Somua | Vallonbourg | 7,903,235 | 66px | 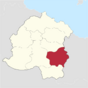
|
| County of Vandarcôte | Gabion | 20,402,143 | File:Vandarcote Coat of Arms.png | 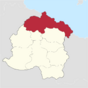
|
| County of Vollardie | Willing | 9,850,322 | 
|
|
| Grand Barony of the Kestrel Isles | Falcsbourg | 736,871 | 
|
|
Government and politics
Government and law

The Yonderian monarch is the Grand Duke. Yonderre is an elective Grand Duchy with elections held immediately following the death of the incumbent Grand Duke. The resultant election is the traditional vote between the nine Counts of Yonderre, one of which ultimately ascends to the status of Grand Duke. Below the Grand Duke is the Yonderian Parliament, a unicameral national legislature headed by the Grand Steward of Yonderre. Established in 1833, it meets in Gillaumebourg in central Collinebourg.
The Parliament passes all laws, approves the cabinet, and supervises the work of the government. It is also responsible for adopting the state's budgets and approving the state's accounts. As set out in the Yonderian Constitution, the Parliament is directly subordinated to the Grand Duke of Yonderre who wields executive power to veto and overturn laws passed by government. In practice, however, the Grand Duke seldom interferes in the work of the parliament. The Parliament consists of 179 elected representatives. General elections must be held every five years, but it is within the powers of the Steward of the Realm to ask the monarch to call for an election before the term has elapsed. On a vote of no confidence, the Parliament may force a single Minister or the entire government to resign.
In accordance with the Yonderian Constitution, legal power is split three-way in Yonderre; executive-, legislative- and judicious power. The executive power is wielded by the Grand Duke of Yonderre, on whose behalf civil servants and the Custodes Yonderre, the Yonderian national police force, maintains law and order. The legislative power is wielded by the Yonderian Parliament. Judiciary power is wielded by the courts of Yonderre.
Policing

The national police force of Yonderre is the Custodes Yonderre. As of 2026, the Custodes Yonderre employs 227,697 people, of which 174,256 are sworn in as officers and 53,423 are civillian employees. Custodes are constitutionally empowered to enforce the law and to effect public and social order, as well as being responsible for border control. Officers of the Custodes Yonderre are referred to as "Custode" in Burgoignesc and "Kustode" in Gothic, and the Chief of Police is referred to as the "Supreme Custodian".
The Custodes Yonderre was first formed in 1643 in the immediate aftermath of the Yonderian Peasants' War. Custodes were initially focused around large cities to enforce law and order, while villages and outlying areas maintained their local watchmen and catchpoles for decades to come. The Custodes Yonderre was reformed in 1833, written into its more modern form as part of the Consitution of Yonderre. The Custodes Yonderre then replaced the previous local and county-based watchmen organisations and nationalized and standardized policing across Yonderre with the introduction of a common code of law across all Counties of Yonderre in 1836.
Custodes Yonderre also processes licenses and permits such as gun licenses, national ID cards and passports, and furthermore, enforces immigration decisions by the Yonderian Immigration Service. Local police must also be notified when organizing public events that may significantly influence local public security and traffic.
Military

The Yonderian Defence Force is the military of the Most Serene Grand Duchy Yonderre. The primary arm of the Yonderian Defence Force is the ground force, which also operates the Army of the Air and the Marine Yonderre. The ground element of the Yonderian Defence Force consists of ten standing divisions divided into two corps, the Grand Ducal Guard Corps and the Second Corps of the Army. In adition, the Yonderian Defence Force also operates a further ten skeletonized divisions, brigade-sized units intended to be mobilized from reserves and combat ready within three days in case of national emergency. Yonderre's official policy states that a wartime military strength of 580,000 personnel constitutes a sufficient deterrent to exterior aggression. The army consists of a highly mobile field army backed up by local defence units. The army defends the national territory and its military strategy employs the use of the heavily forested terrain and numerous lakes to wear down an aggressor, instead of attempting to hold the attacking army on the frontier.
The Army of the Air operates some 275 fixed-wing combat aircraft divided into 21 wings as well as a similar number of logistical aircraft. The Army of the Air also operates an arsenal of combat helicopters as well as search and rescue helicopters. The Marine Yonderre is the Navy of Yonderre and operates two Sentinelle-class helicopter carriers, four Vigilante-class frigates, six Infatigable-class corvettes and a wide array of smaller support and auxillary ships. The Marine Yonderre is also the administrating body of the Grand Vandarch Canal.
The Yonderian Defence Force is committed to peacekeeping operations worldwide and has been in the Pukhtun Sea as part of Operation Khyzer Rhykh since 2010. The Yonderian Defence Force has been an active party in the Deluge since 2016, the Army of the Air having led a succesful air campaign against Algoquonan militias in Operation Mission Shield and all YDF branches having fought as part of the later Operation Western Blizzard. The Yonderian Defence Force was also directly involved militarily in Cetsencalia and Quetzenkel during the Final War of the Deluge, fighting on land, air and sea.
Economy

The economy of Yonderre is a highly developed social market economy with state-ownership in strategic areas. The service sector has come to play a significant economic role, particularly the Yonderian food industry and tourism, though the country remains one of the largest arms manufacturers on the planet. With a gross domestic product of $6.287 trillion, Yonderre possesses the 13th-largest economy worldwide and the fourth largest economy in the Levantine Union, while it's GDP per capita ranks 3rd globally, after Cartadania and Caphiria, at $62,040.56, by far the largest in the LU. It is the richest country per capita to not border an ocean.
Once a predominantly agricultural country on account of its arable landscape, a liberalisation of import tariffs in 1788 following the Second Potato War marked the end of mercantilism and further liberalisation in the ninetenth and the beginning of the tweentieth century established the Yonderian liberal tradition in international trade that was only to be broken by the Second Great War. Even when other countries raised protection for their agricultural sector because of increased Urcean competition resulting in much lower agricultural prices after 1870, Yonderre retained its free trade policies as the country profited from the cheap imports of cereals (used as feedstuffs for cattle and pigs) and could increase their exports of butter and meat of which the prices were more stable.
Yonderian partially-state owned heavy industry conglomerate AMY had a 2025 annual revenue of ₮66 billion while companies like Primo Kino and Federation Rasslin Yonderre (FRY) represent international entertainment powerhouses with revenuse of several billion Talers. Other billion Taler companies include SuperNOVA (pharmaceudicals), Toubourg Brewery (beer and liqueurs), Chef Chev (restaurant), Willing Group (retail) and Banc Yonderresc (banking).
Demographics


| Rank | City | County | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Collinebourg | Collinebourg | 8,230,000 |
| 2 | Gabion | Vandarcôte | 7,842,000 |
| 3 | Donnebourg | Donne | 3,638,400 |
| 4 | Sainte-Catherine | Kubagne | 3,192,700 |
| 5 | Willing | Vollardie | 2,965,250 |
| 6 | Famichez | Vandarcôte | 2,885,500 |
| 7 | Toubourg | Amarre | 2,770,000 |
| 8 | Vandarcholme | Vandarcôte | 2,410,200 |
| 9 | Vallonbourg | Somua | 2,150,000 |
| 10 | Sainte-Cateline | Vandarcôte | 1,930,300 |
Education

All educational programmes in Yonderre are regulated by the Ministry of Education and administered by local municipalities. Public schools cover the entire period of compulsory education, encompassing primary and lower secondary education. Most children attend public school for 10 years, from the ages of 6 to 16. There are no final examinations, but pupils can choose to sit an exam when finishing their last year. The test is obligatory if further education is to be attended. Alternatively pupils can attend a private school such as schools operated by the Order of Saint Prokop.
All university education in Yonderre is tuition free, covered by taxation. Students aged 18 or above may apply for state educational support grants that provides fixed financial support, disbursed monthly. Yonderian universities offer international students a range of opportunities for obtaining internationally recognized qualifications in Yonderre. The University of Collinebourg is Yonderre's largest and oldest university founded in 1479. The Academic Ranking of World Universities placed it 30th in the world in 2026. Gabion University is the second oldest and second largest university in Yonderre by number of students and typically ranks within the 100 best universities in Levantia.
Culture
Yonderre shares strong cultural bonds with Burgundie from which many settlers emigrated from the fifteenth century and throughout the early modern period. Culture and the arts thrive as a result of the proportionately high amount of government funding they receive, much of which is administered by local authorities so as to involve citizens directly. Thanks to a system of grants, Yonderian artists are able to devote themselves to their work while museums, theatres, and the film institute receive national support.
Northern Ideal

The Northern Ideal is a series of observations and concepts related to how the people of Yonderre view themselves and their history. Within the Northern Ideal, the Yonderian people view themselves as the direct inheritors of their crusading past, making the country a bastion of the Catholic faith as well as the chivalrous and orderly social mores of the Crusading knights. The aspiration to meet this standard permeates all levels of social, economic, and political life in Yonderre.
Since the Yonderian Golden Age of the 19th century, the Grand Duchy has undergone significant social and political evolution which moved it away from its traditional structures. Despite this, the Northern Ideal remains in place with little public notion of reimagining or reapplying it to modern life. The significant differences between the Ideal and modern Yonderian life has been the subject of significant study. For example, Yonderre was among the first nations to legalize pornography in 1969 and has comparatively loose abortion laws, a cause of concern for some neighbouring countries like Urcea.
Cinema
Primo Kino is the prime purveyor of Yonderian cinema to the world audiences, delivering such classics as How I (almost) accidentally started the Third Great War, Dates for Monarchs, A Man Called Pierre and Margherita. The Yonderian movie industry is centered around Komeon Boulevard in Gabion on the Vandarch Coast. Some prolific and acclaimed actors like Jean-Yves Forvert or Edith le Fêvre each have hundreds of appearances in movies and TV shows.
Music
Crooners like Dom Martinez and François Artanis took Yonderre by storm in the 1950s and 60s, having come up from shows in the clubs of Gabion in the 1940s with a blend of proto-stand up slapstick comedy and singing. A vivid rock music scene emerged in the 1970s that lead to a plethora of rock and music genres played throughout the 1980s, producing iconic bands like Crusaders and Exception. Edith d'Alisse is an up and coming star in pop music, winning the WorldVision 2026.
Sports
The Yonderre national football team is among the best in the world, having been ranked in the top since the 1980s. The Yonderian football league is among the highest rated of all football leagues. The Federation Rasslin Yonderre (FRY) is one of the most watched purveyors of sports entertainment in the world since the 1980s, delivering professional wrestling and dramatic plotlines to worldwide audiences from weekly shows and special pay-per-view events.