Pursat
This article is a work-in-progress because it is incomplete and pending further input from an author. Note: The contents of this article are not considered canonical and may be inaccurate. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. |
Muwahhidnn State of Pursat Pursat | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
Motto: Freedom at last | |
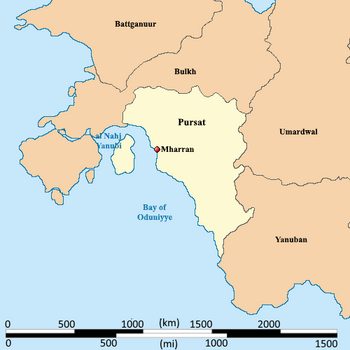 Map of Pursat | |
| Capital and | Mharran |
| Pursi, Burgoignesc | Arabic |
| Ethnic groups | Druze |
| Demonym(s) | Pursatnieen |
| Government | Theocracy |
| Establishment | |
• Independence from the MNLC | 1822 |
| Area | |
• | 610,667.397 km2 (235,780.000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 504,569,500 |
• Density | 826.259/km2 (2,140.0/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $6,358,080,269,500 |
• Per capita | $12,601 |
| Currency | Pursatni Taler (PT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+0 |
| Date format | dd-mm-yy |
| Driving side | right side |
| ISO 3166 code' | P₮ |
The Muwahhidnn State of Pursat, often just called Pursat, is a rapidly modernizing nation in southwestern Daria region of Audonia bordered by the Bay of Oduniyye in the west, Bulkh in the north, Umardwal and Yanuban in the east and south. It was massively urbanized in the 1980s and 90s and has a very high population for its landmass. Its executive is a president for life, but it does hold democratic elections for its legislative branch and local offices.
Pursat is a member of many international organizations like the League of Nations, the ISO, Red Crescent International, etc. and many other regulatory and economic bodies.
It is a market economy focused on exports, under the watchful eye of Burgundie, whose companies have a massive stake in the country's economic activity. It specializes in the assembly of microprocessors and cellphones, as well as the cultivation of tropical hard woods, fishing, and rubber, which also constitutes its major exports.
The people of Pursat are predominantly culturally Touareg, speak Pursi, and most practice Druzism.
Etymology
Pursat is a transliteration of the Aramaic word pirsa meaning lust with the tay merbutah the final "t" sound meaning the place lusted after. It was referred to as such because of its beautiful landscape and rich resources. Some scholars have postulated that it could have been the location of the real life inspiration for the Biblical Garden of Eden.
Geography
Pursat is bordered by Bulkh to the northwest, Umardwal to the east, Yanuban to the southeast and Umardwal and the Great Kavir desert to the north. Pursat's borders are marked by several significant rivers. The Iteru and Lilu Rivers form the country's northwestern border with Bulkh, while the al-Firat River delineates its eastern border with Umardwal. Off the northwestern coast of Pursat, in the Bay of Oduniyye, lies the low-laying island province of Fapimunein, which is semi-arid. The most prominent geographical feature of mainland Pursat is its expansive coastal plain, stretching along the country's northwestern to southeastern coastline. This plain is characterized by a gradual slope, rising from the sea level towards the interior. The plain is predominantly semi-arid, with limited rainfall supporting scrub vegetation and scattered oases. Two mountain ranges, the Zagrin Mountains in the northwest and the Baqunah Mountains in the southeast, define the boundaries of the coastal plain. These ranges create a natural barrier, influencing the climate and providing a source of water for the surrounding regions. The Zagrin Mountains, particularly, offer a more temperate climate, contrasting with the aridity of the coastal plain. To the north of the coastal plain lies the Great Kavir desert, a vast expanse of arid land characterized by sand dunes, salt flats, and extreme temperatures that spans Battganuur, Bulkh, Pursat, and Umardwal. The desert, through desertification, has continued to push southward, reducing the semi-arid coastal plain by 35% in the last 300 years, but 14 percent of the total was in just the last 75 years.
Climate
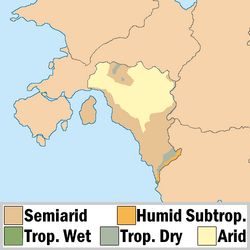
Pursat's climate has a semi-arid climate in the coastal plain, with hot summers and mild winters. The Great Kavir desert to the north amplifies the aridity, with extreme temperatures and minimal rainfall. The Zagrin and Baqunah Mountains, the countries northwestern and southeastern regions respectively, provide a more temperate environment, with cooler temperatures and higher precipitation compared to the surrounding areas.
Annual precipitation varies from 500 to 900 mm (19.7 to 35.4 in) depending on the region with an average of 590 mm (23.2 in). Cyclones are also common during the wet season. Average temperature ranges in Mharran are from 13 to 24 °C (55.4 to 75.2 °F) in July to 22 to 31 °C (71.6 to 87.8 °F) in February.
| Climate data for Mharran | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29.9 (85.8) |
29.6 (85.3) |
29.3 (84.7) |
27.8 (82.0) |
26.4 (79.5) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
29.1 (84.4) |
27.2 (81.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.3 (79.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
21.4 (70.5) |
18.9 (66.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
20.0 (68.0) |
21.5 (70.7) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
25.5 (77.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.3 (72.1) |
22.3 (72.1) |
21.5 (70.7) |
19.4 (66.9) |
16.9 (62.4) |
14.4 (57.9) |
14.2 (57.6) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.2 (63.0) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
21.4 (70.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 171.1 (6.74) |
130.5 (5.14) |
105.6 (4.16) |
56.5 (2.22) |
31.9 (1.26) |
17.6 (0.69) |
19.6 (0.77) |
15.0 (0.59) |
44.4 (1.75) |
54.7 (2.15) |
81.7 (3.22) |
85.0 (3.35) |
813.6 (32.04) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 8.1 | 7.6 | 7.0 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 5.5 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 60.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 76 | 77 | 76 | 74 | 73 | 72 | 71 | 73 | 75 | 75 | 74 | 74 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 223 | 210 | 225 | 229 | 253 | 246 | 256 | 252 | 228 | 210 | 198 | 220 | 2,750 |
| Source: ur mom | |||||||||||||
History
Prehistory
The earliest human settlements in modern-day Pursat trace back to the Paleolithic era, evidenced by rudimentary stone tools found near the fertile banks of the local rivers. As agriculture emerged during the Neolithic period, the inhabitants established small villages and began cultivating grains (wheat and pulse is attested in the archeological record) and domesticating animals, namely dogs and several types of water fowl. By the early Bronze Age, a distinct culture began to take shape, characterized by its unique pottery and jewelry. Throughout this epoch, the people in Pursat experienced gradual cultural and technological advancements, laying the foundation for the emergence of a future complex civilization.
Classical Antiquity
-
The Great Stones
-
Remnants of the Great Library of Kussaipis
-
Ruins of the power naval city Aknosheh
-
Kemeti ropework
In the 9th century BCE, the Kemeti people rose to prominence as a regional power, establishing trade networks with neighboring civilizations and developing a sophisticated system of writing based on hieroglyphs. The Kemeti pantheon, featuring gods like Re, the sun god, and Isus, the goddess of fertility, became central to Kemeti religious life. During this era, monumental structures like the Great Stones and the Temple of Amin were constructed, showcasing the Kemeti's architectural prowess. They were great slavers and traders of fine goods all along the Bay of Oduniyyad and they were also connected into the Sea of Istroya trade network. As desertification of the Great Kavir pushed some closer to the coast, the Kemeti became war-like and centralized capturing most of modern Bulkh, Pursat, Yanuban, parts of southern Umardwal, and Syliria. The Kemeti dominated the local Arabs and Pursi people.
In 42 AD, the Coptic Christian faith was founded in Pursat and local Arabs and Pursi adopted it very quickly despite violent pushback from the Kemetis.
By the 7th century AD, the once-mighty Kemeti civilization had endured millennia of prosperity and dominance. However, internal strife, political instability, and the pressure of neighboring empires had gradually weakened the Pharaonic state. The final dynasty, the Pe-ankh-em-tanenids, weakened by corruption and economic decline, struggled to maintain control over its vast territory. In 739, the armies of the Oduniyyad Caliphate, set their sights on the Kemetis. Led by the brilliant general 'Amr ibn al-'As, the Arab Muslim forces swiftly crossed the frontier and engaged the Kemeti army at the Battle of Fapohdet. Despite their valiant efforts, the Kemeti forces were no match for the disciplined and highly motivated Arab Muslim army. The defeat at Fapohdet marked the beginning of the end for the Kemeti civilization.The Oduniyyad Caliphate forces continued their advance, capturing major cities and fortresses across the . In 842 AD, the cultural and intellectual heart of the Kemeti civilization, Medvasut, fell to the invaders. The Great Library of Kussaipis was burned down by the rampaging Caliphal forces marking the end of the Kemeti civilization, at least as a centralized state. Remnants of the Pharaonic retinue and army fight for three more years but they were never victorious and the Pharaoh Atemu III died, alone in the streets, in 843, his family and heirs all killed by the Oduniyyad Caliphate.
Medieval period
-
Mamluking good
-
Kemeti papermaking
The medieval period in Pursat was marked by the wars with and eventual occupation by the Oduniyyad Caliphate. During this time, Pursat became a crossroads of cultures and religions, while Islam was the state religion, the Beys of Pursat, as the Caliphal province was called, allowed some dhimmi, with Coptic Christianity and traditional Kemeti beliefs allowed in the province, but active conversion efforts throughout the tenure of the Caliphate meaning that over 80% of the province were reported as Sunni Muslims by 1150. Intellectual pursuits flourished under Arab rule, with Pursat's scholars making significant contributions to fields like mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. Pursati architecture also underwent a transformation, incorporating Islamic influences into its designs. The Beys of Pursat were very wealthy and respected among the Caliphal court.
It was during this time that the Druze faith was founded in Pursat and many of the Coptic Christians converted as it was most aligned with Islam and therefore more tolerated by the Arab Beys.
Early modern history
Eloillette (1526 until 1795)
Silver mining, sorghum, millet, yams, fava beans, jute, sweet potatoes, cowpeas, bambara groundnut, bananas, and slaves
Late modern period
Words, words, words. (late 19th century - 1943 (end of Second Great War)
Contemporary period
Words, words, words. (1943-today)
Government and politics

The central government of Pursat is in its capital city Mharran, home to around 4.2 million people. The government's complex known as "The Great Fort" is the ancient citadel of the city and currently hosts both branches of the government.
Executive and judicial branch
Pursat has a single branch that performs the functions of an executive and a judicial branch. The Council of Uqqāl (Aenglish: Enlightened) are a body of Druze legal and theological scholars and from among them is elected a Supreme Professor who serves as the head of state, the leader of the government, and the highest justice in the country. The Council of Uqqāl also reviews and adjudicates legal matters through a network of local Councils of Lesser Professors who also perform the functions of executive branch functionary employees.
Legislative branch
The legislative branch is a secular forum of tribal leaders whose job it is to consult with their clansmen and to draft and propose laws to the Council of Uqqāl. Its primary focus is on infrastructure, international politics, and defense over which it maintains almost complete autonomy.
Local governance
Local governance is relegated to traditional leaders, typically tribal or clan patriarchs/matriarchs in rural areas and to elected mayor-council regimes in urbanized regions. There is no intermediary form of state or provincial government as all government services are relegated to the executive branch's network of Councils of Lesser Professors.
Military
-
Umardi woman in the 6th Infantry Regiment
Pursat as a large but underfunded, undertrained, and under-equipped military that primarily consists of the army at 1.2 million personnel, a small but professional air force of 120,000 personnel, a Littoral Defence a s Enforcement Fleet (equivalent to most nations coast guards but also with a strong defense mission) of 238,000 personnel, and a navy of 638,000 personnel. These forces suffer from a lack of centralization and have, in recent exercises conducted by Burgundie in 2018 and 2025, failed to coordinate and meet strategic objectives. The government has made considerable investments in modernizing the military but the high command is resistant to changing their ways which is impeding progress.
Because of its more liberal stance on women's rights, the Army of Pursat has, since the Islamic Revolution in Umardwal, had a contingent of Umardi women, which was formalized in 1994 as the 6th Infantry Regiment, Umardiennes (also known as the Women's Legion). The unit is 2,740 strong and consists 70% of Umardieen, 25% Pursatnieen, and 5% other foreign nationals. The unit is used as a border guard unit on the Yanubi frontier.
Society
The Touareg are the largest ethnic group, comprising 73.6% of the populace. The Ebidi, make up a significant 14.7% minority, while Arabs, historically linked to trade and migration in Daria, account for 6.3%. Occidentals, primarily of Bergendii descent and connected to historical colonial ties and economic partnerships, represent 2.4% of the population. The remaining 3% is a mix of various ethnicities. Pursi is the dominant native language, spoken by the majority. Burgoignesc is widely used in commerce, education, and government due to historical ties with Burgundie. Arabic holds significance as a liturgical language for the Muslim minority and is also used in trade and cultural exchange. Druzism is the majority faith, deeply embedded in the social fabric. A significant minority practices Islam, primarily Sunni, while a smaller population, mainly Occidental expatriates and converts, follow Christianity. The late 20th century saw rapid urbanization, resulting in high population density, particularly in the capital city, Mharran.
Pursat's culture is an amalgam of native ancient Druze and Kemeti, medieval Arabic, and early-modern Occidental cultures that have layered on top of each othe over the last millennium. Druzism, the majority faith, permeates daily life with its unique rituals and beliefs, celebrated in festivals like Ziyarat al-Nabi Shu'ayb, where Druze pilgrims journey to the holy site of Nabi Shu'ayb. The Oddiyad Caliphate brought Islam and Muslim architecture and the observance of high holidays like Ramadan, during the medieval period.
Pursat's cuisine is based on Touareg staples like taguella stew. Ebidi dishes like fufu and peanut soup, brought by the colonial-era slavery network and Arabic spices and ingredients like cumin, coriander, and dates have also become regular aspects of Pursat cuisine.
Historically literature was not a major aspect of Pursatieen culture. Oral storytelling, passed down through generations of Touaregs and while they still remain an important cultural aspect of Pursatieen life, written works in Pursi, Arabic, and Burgoignesc became a part of the ouvre during the colonial-era. Pursatnieen literature often explores themes of identity, cultural preservation, and the challenges of modernization. Art in Pursat thrives with lots of government subsidization. Intricate Touareg jewelry, made of locally sourced gold and semi-precious stones are internationally recognized signs of Pursat. Attire in Pursat draws on Audonian traditionalism and Occidental modernity. Touareg men often wear the distinctive tagelmust, a blue veil that protects from the harsh desert sun, while women wear colorful headscarves and intricate silver jewelry. Ebidi women favor vibrant patterns and flowing fabrics, while men often wear dashikis or embroidered tunics. Western-style clothing is also common, particularly in urban areas.
Cuisine
Pursi cuisine
Kemeti cuisine
Kemeti cuisine relies heavily on legume and vegetable dishes. For most Kemetis there is a strong connection to food that is derived from ingredients that grow out of the ground as they see themselves as the Great and Ancient Agriculturalists of the region. As a result, a great number of vegetarian dishes have been developed that are the pride of the Kemeti people. Kushari (a mixture of rice, lentils, and macaroni) is the "national dish" of the Kemetis and it is served at all of the ceremonies and events of Kemeti life. It is prepared when guests are staying over, for birth, circumcisions, birthdays, weddings, and funerals. In addition, ful medames (mashed fava beans) is one of the most popular dishes. Fava bean is also used in making taʿmiya, also known as falafel, is a staple in many Darian cuisines, but originated in the culinary traditions of the Kemeti civilization. Garlic fried with coriander is added to molokhiya, a green soup made from finely chopped jute leaves, sometimes with chicken or rabbit for special occasions.
Sport
Pursatni Pangolins

The national WAFF league soccer team of Pursat are the Pursatni Pangolins. They have never won the WAFF World Cup but they do well in the WAFF Audonian Cup most years.
Economy
Agriculture and herding
Pursat's tropical climate allows for a diverse range of agricultural activities. In the fertile lowlands, farmers cultivate like sorghum, millet, yams, sweet potatoes, cowpeas, bambara groundnut, fave beans, and bananas. Nomadic herders in the northern steppes raise livestock such as camels, goats, and sheep but due to the small scale and nomadic lifestyle these rarely make it to export markets and are consumed locally by those communities. The country possesses significant mineral resources, including copper, gold, and phosphates. Mining operations contribute to the country's export earnings and are a major employer for the country. The financial sector is rapidly evolving, with the establishment of modern banking institutions and the growth of microfinance initiatives with investments primarily coming from Burgundie. While traditional financial practices like hawala remain prevalent in some areas, the government is actively promoting financial inclusion and modernization. The manufacturing sector is primarily focused on the assembly of electronics, particularly microprocessors and cellphones. This industry has benefited from foreign investment, primarily from Burgundie, and technology transfer, contributing to the country's economic growth and diversification. The government of Pursat hosts workshops for native skilled artisans to produce intricate textiles (rugs, wool, and tanned leather), traditional pottery (tagines in particular), jewelry, and camel and goat leather goods, which are sought after by both domestic and international consumers. Pursat's government is working with domestic and international companies to invest in tourism infrastructure that will lean into the purported Biblical connections and become a hotspot for Christian pilgrims and religious tourism. Pursat's coastline offers abundant fishing opportunities, supporting both local fishing communities and a growing aquaculture industry. Deep-sea fishing vessels primarily catch tuna and other pelagic fish, while coastal communities engage in artisanal fishing practices. Aquaculture farms, particularly shrimp farms, have emerged as a significant contributor to seafood exports. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, Pursat is actively developing its green sector. Investments in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are reducing the country's reliance on fossil fuels, but these efforts are still nascent.
Recycling and waste management
Ship breaking

One of the largest industries by value and by population involvement in Pursat is ship breaking. There are 8 ship breaking yards along the mainland and 3 along the island of Fapimunein. The yards on the mainland are bigger and designed to serve the needs of Pursats' Occidental clientele who typically have large numbers of bigger ships. The yards on Fapimunein serve clients from Audonia and have a much lower through rate. These yards are primarily focused on scrapping the ships but the steel in particular is recycled and provides over 100% of the annual need for steel in the country. The excess steel is sold to neighboring countries and has been praised with reducing the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process across southern Daria. Fixtures and other maritime equipment that is salvageable is sold to regional shipyards for reuse as well. As such, ships produced in Daria often have very high capabilities and facilities on board even if the equipment is a bit dated.
Infrastructure
Rail
Pursat uses Standard gauge, 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) as most of its rail infrastructure has been under the auspices of Burgundie and its sphere of influence in the Middle seas region, who all use that rail gauge.
Roads
Louage
A louage is a minibus shared taxi in many parts of Daria that were colonized by Burgundie. In Burgoignesc, the name means "rental." Departing only when filled with passengers not at specific times, they can be hired at stations. Louage ply set routes, and fares are set by the government. In contrast to other share taxis in Audonia, louage are sparsely decorated. Louages use a color-coding system to show customers what type of transport they provide and the destination of the vehicle. Louages with red lettering travel from one state to another, blue travel from city to city within a state, and yellow serves rural locales. Fares are purchased from ticket agents who walk throughout the louage stations or stands. Typical vehicles include: the MILCAR Jornalero, the TerreRaubeuer Valliant 130, and the CTC M237-07.
Power and electricity
See also



























