Battganuur: Difference between revisions
Tag: 2017 source edit |
|||
| Line 214: | Line 214: | ||
====Barbary Straits colony==== | ====Barbary Straits colony==== | ||
{{Further|Barbary Straits colony}} | {{Further|Barbary Straits colony}}Amid the outbreak of the Barbary Wars, while much of the anti-piracy conflict was centered around the Barbary Straits between the Buroignesc Navy and corsairs hailing from what is modern Battganuur, the range of Barbary pirates stretched even further north reaching even the domain of [[Soirwind]]. Soirwind being at the time a colonial domain under what is modern day [[Fiannria]], the spike in piracy interrupting crucial trade routes between Fiannria and Soirwind quickly drew the ire of the Levantine state. In ____ Fiannria sent a punitive expedition towards the region to combat the corsairs. Rebuffed from operating in the main combat zone and drawing too close to the Barbary Straits itself, the Fiannan war fleet set for the north towards the northern Sea of Istroya to hunt down Corsairs who broke through and expanded operations that more directly impacted Fiannria itself. The war fleet would operate between the [[Hezikian Isles]] and Soirwind for the next three years in its attempt to guard trade routes and eliminate pirate holdouts and outposts. | ||
{{Further|Burgoignesc colonial empire}} | |||
As the conflict in the Straits themselves raged on, the Fiannan central government would delegate more and more operational authority towards the holy orders which persisted as remants from the Crusaders and independent privateers in combating northern Barbary Piracy. This culminated in the year of _____ following the victory in the Barbary straits themselves, a large contingent of Barbary ships which survived the punitive Burgoignesc expeditions escaped to the north in order to flee arrest and execution and also find a new base of operations, instead off the southern coast of Soirwind, found a fleet of privateers and corsair chasers waiting between the coast and the island of Antilles. This fleet of holy orders, privateers and colonial defense ships from Soirwind, having gotten word of the coming fleet had gathered in the strait to attack and nip the bud of any continued corsair activity in the north. The resultant battle, the [[Battle in the Kamtague Narrows]], saw the bulk of the remaining corsair force sunk or captured, and the remnants scattering, breaking any chance of a major Barbary incursion returning to operate in the north. {{Further|Burgoignesc colonial empire}} | |||
Colony of the [[History of Dericania#Duchy of Marialanus|Duchy of Marialanus]]: [[1577]]-[[1876]] | Colony of the [[History of Dericania#Duchy of Marialanus|Duchy of Marialanus]]: [[1577]]-[[1876]] | ||
| Line 225: | Line 226: | ||
File:Orłowski Persian dignitary.jpg | File:Orłowski Persian dignitary.jpg | ||
File:1884 Persian Officers & Soldiers.jpg | File:1884 Persian Officers & Soldiers.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery>Independence in the southern regions of what would be modern day Battganuur came at an interesting time for the modern state of Fiannria. In desperate need for funds and resources following the wars which consumed the young Commonwealth's early years and somewhat political isolated following the success of the republic within the Holy Levantine Empire, the Commonwealth would seek for new relationships among the new young kingdoms and states that make up southern Battganuur. Both merchants and veterans of the early wars in Fiannria would find audiences in the courts of newly independent emirs who were interested in access to western-style tactics, western military equipment, and resources. In exchange for vital Levantine manufactured goods and weaponry, along with expertise, Fiannan merchants got a crucial lifeline in resources and income to allow the young Republic to survive and continue to fund its reconstruction. The relationships established by newly establish states formed in the wake of the independence movements in Audonia and the Commonwealth of Fiannria when it was in desperate need of allies and trading partners would come to define much of the relationship of Fiannria and Audonia from then on and establish a policy of state-building, support and relationship building between Audonian states and Fiannria during this period and after. | ||
===Contemporary era=== | ===Contemporary era=== | ||
<gallery mode="packed"> | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
Revision as of 06:59, 29 June 2024
This article is a work-in-progress because it is incomplete and pending further input from an author. Note: The contents of this article are not considered canonical and may be inaccurate. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. |
Republic of Battganuur | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
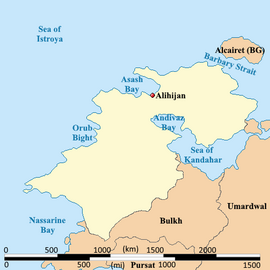 Location of Battganuur (dark green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Alihijan |
| Official languages Recognised minority languages | Umardi, Burgoignesc |
| Demonym(s) | Battganuuri |
| Government | |
• Chief of Ministers | Faisal-Jallal Asayesh Aslani |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,525,943.29 km2 (589,170.00 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2025 estimate | 204,504,300 |
• Density | 134.018/km2 (347.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 3,748,972,827,600 estimate |
• Per capita | 18,332 |
| Time zone | UTC- |
Battganuur is an industrialized and modern nation in western Audonia, stratling the coasts of the eastern Sea of Istroya, the southern coast of the Barbary Strait, the western coast of the Sea of Kandahar, with a small land boarder with Umardwal in the north east, and a long southeastern border with Bulkh. Its coastal areas are heavily urbanized with its interior being largely rural.
Battganuur has a bicameral legislature, a supreme court, and an executive, the Chief of Ministers who acts in the same capacity as a president.
It is a member of the League of Nations, the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, and many other international organizations.
It is a market economy focused on exports, under the watchful eye of Burgundie whose companies have a massive stake in the country's economic activity. It specializes in the assembly of microprocessors and cellphones, as well as the cultivation of tropical hard woods, fishing, and rubber, which also constitutes its major exports. It is an active leader in the Middle seas region's economic activity.
Many scholars have criticized its economic governance and politics, arguing that it is merely a client of the Burgoignesc thalattocracy's economic and cultural might.
The people of Battganuur are predominantly culturally Persian, speak Umardi, and most practice Shia Islam.
Geography
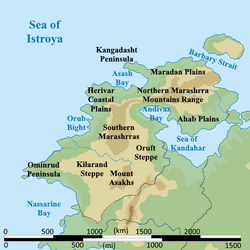
Climate and environment
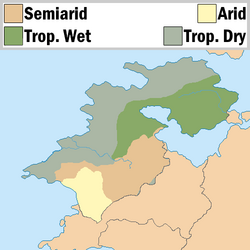
The tradewinds bring moisture from the Aab-e-Farus and the Sea of Kandahar to the northern interior of Battganuur. In the nation's coast picks up residual moisture from the Sea of Istroya but the tradewinds keep it from having a sever rainy season. The southern third of the country, predominantly Nahaqqez State, is dominated by the Great Kavir. The prevailing winds pushing moisture off of the Sea of Kandahar keeps the northern portion of the southern third semi-arid.
History
Prehistory
Battganuur was originally settled by Indo-Aryan peoples who likewise settled areas from Zaclaria to Pukhgundi. These people shared languages with common roots, the Indo-Aryan languages which later diverged into Proto-Umardonian (west of the Sindhus River) and proto-Sindhus (east of the Sindhus River).
Umaronid Empire
Classical Antiquity
-
Istroyan soldiers
Kingdom of Eshel
The Kingdom of Eshel was a Jewish ethnoreligious state formed round 500 BC under King Adud I on the Ominrud Peninsula. It was a regional powerhouse in the eastern Sea of Istroya during the late Classical Period with a strong trade network with the Istroyan civilization. It remained staunchly independent despite many attempts to subjugate them by the Ashrafinid Empire to the north. It is notable that Eshel fought on the side of the Christians in the Crusades in Audonia from 1167–1428. In fact, the end of the Crusades was a contributing factor to the decimation of the Kingdom by the Oduniyyad Caliphate in 1486.
Arunid Empire
Istroyan city states
Ashrafinid Empire
Audonian Christianity Ruled most of Battganuur and the Alcairet. The aristocracy refused to convert to Islam and were eventually pushed out and some emirated to Levantia to form Hištanšahr
Golden Age
Denoted as starting with the Muhammadian conquest of the city of Ramsakhs in 670s and ending at the fall of the Oduniyyad Caliphate in 1517, the Golden Age of Audonia had a sweeping effect on the area of modern Battganuur. When it was conquered by the Oduniyyad Caliphate in the 700 and 800s the area was generally already very developed and it took a lot of time and effort to convert the area to Islam.
Crusades
Battganuur was the most heavily impacted by the Crusades in Audonia.
Colonial era
-
Battganuuri boat in 1845
Starting with the fall of the Oduniyyad Caliphate in 1517 and lasting until the expulsion of the Marialanii Ularien Trading Company in 1836 and the Bourgondii Royal Trading Company in 1842, the early modern era in Battganuur was characterized by rapid development, and unprecedented resource and human exploitation.
Istroya Oriental colony

Colony of the Duchy of Martilles: 1611-1795
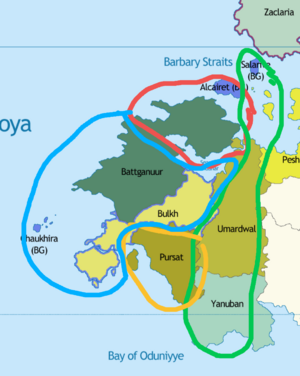
Barbary Straits colony
Amid the outbreak of the Barbary Wars, while much of the anti-piracy conflict was centered around the Barbary Straits between the Buroignesc Navy and corsairs hailing from what is modern Battganuur, the range of Barbary pirates stretched even further north reaching even the domain of Soirwind. Soirwind being at the time a colonial domain under what is modern day Fiannria, the spike in piracy interrupting crucial trade routes between Fiannria and Soirwind quickly drew the ire of the Levantine state. In ____ Fiannria sent a punitive expedition towards the region to combat the corsairs. Rebuffed from operating in the main combat zone and drawing too close to the Barbary Straits itself, the Fiannan war fleet set for the north towards the northern Sea of Istroya to hunt down Corsairs who broke through and expanded operations that more directly impacted Fiannria itself. The war fleet would operate between the Hezikian Isles and Soirwind for the next three years in its attempt to guard trade routes and eliminate pirate holdouts and outposts. As the conflict in the Straits themselves raged on, the Fiannan central government would delegate more and more operational authority towards the holy orders which persisted as remants from the Crusaders and independent privateers in combating northern Barbary Piracy. This culminated in the year of _____ following the victory in the Barbary straits themselves, a large contingent of Barbary ships which survived the punitive Burgoignesc expeditions escaped to the north in order to flee arrest and execution and also find a new base of operations, instead off the southern coast of Soirwind, found a fleet of privateers and corsair chasers waiting between the coast and the island of Antilles. This fleet of holy orders, privateers and colonial defense ships from Soirwind, having gotten word of the coming fleet had gathered in the strait to attack and nip the bud of any continued corsair activity in the north. The resultant battle, the Battle in the Kamtague Narrows, saw the bulk of the remaining corsair force sunk or captured, and the remnants scattering, breaking any chance of a major Barbary incursion returning to operate in the north.
Colony of the Duchy of Marialanus: 1577-1876
Independence, post-colonial era
Independence in the southern regions of what would be modern day Battganuur came at an interesting time for the modern state of Fiannria. In desperate need for funds and resources following the wars which consumed the young Commonwealth's early years and somewhat political isolated following the success of the republic within the Holy Levantine Empire, the Commonwealth would seek for new relationships among the new young kingdoms and states that make up southern Battganuur. Both merchants and veterans of the early wars in Fiannria would find audiences in the courts of newly independent emirs who were interested in access to western-style tactics, western military equipment, and resources. In exchange for vital Levantine manufactured goods and weaponry, along with expertise, Fiannan merchants got a crucial lifeline in resources and income to allow the young Republic to survive and continue to fund its reconstruction. The relationships established by newly establish states formed in the wake of the independence movements in Audonia and the Commonwealth of Fiannria when it was in desperate need of allies and trading partners would come to define much of the relationship of Fiannria and Audonia from then on and establish a policy of state-building, support and relationship building between Audonian states and Fiannria during this period and after.
Contemporary era
Government and Politics
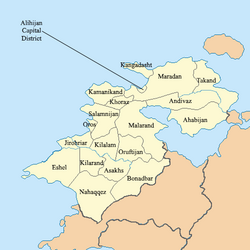
Subdivisions
-
Nahaqqezrabad, capital of Nahaqqez
- Ahabijan
- Andivaz
- Takand
- Maradan
- Kangadasht
- Kamanikand
- Khoraz
- Malarand
- Salamnijan
- Oros
- Jirohriar
- Kiliam
- Kilarand
- Oruftijan
- Asakhs
- Bonadbar
- Nahaqqez
Alihijan Capital District
Capital city, most populated city in Battganuur.
Military



Society
Linguistic Demographics
Religious Demographics
Architecture
Economy
Standard of living
Employment
Tourism
Agriculture
-
Rice
-
Cattle
-
Cashews
-
Mangoe latifundia
Rice: Around 26 million hectares of rice paddy land stretch across fertile plains of the northeastern provinces of Ahabijan, Andivaz, Takand, Maradan, and Malarand. Over 52 million people are employed in rice cultivation making it one of the largest employment sectors in the country. The rice sector yields an average 117 million tons annually, around 100 million tons, is exported, making it a critical pillar of the economy of the country.
Cashews: In the drier western part of the country, cashew trees thrive. Traditional methods prevail which involve hand-harvesting, sun-drying, and shelling the nuts, resulting in an export of around 200,000 tons each year.
Mangoes: Mangoes are grown in the country's west. Farmers utilize grafting techniques and careful water management to cultivate diverse varieties. An estimated 1 million tons of mangoes are produced annually, with around 700,000 tons exported.
Bananas and Plantains: Bananas and plantains grown in the northeast of Battganuur. Farmers employ sustainable practices like intercropping and organic fertilizers to cultivate around 2 million tons of bananas and plantains combined. Roughly 1 million tons find their way to international markets.
Rubber: Rubber latifundia thrive in the humid northeast. Skilled workers carefully extract latex using sustainable tapping methods, producing an estimated 300,000 tons of rubber annually. Around 250,000 tons are exported.
Cattle and Goats: Roaming freely across vast pastures in the west and southeast, cattle and goats are raised by herders. Traditional practices like rotational grazing and selective breeding ensure animal welfare and sustainability. Battganuur exports around 100,000 tons of beef and 50,000 tons of goat meat annually.
Fishing: The coastal waters surrounding Battganuur teem with diverse fish species. Modern fishing fleets and traditional techniques, maintain a catch of around 500,000 tons annually. Around 300,000 tons are exported.
Guar and guar gum: worlds largest producer
Agrinergie


Main article: Agrivoltaics Battganuur began to embrace agrinergie in 2016 when the Agricultural University of Maradan State partnered with the Burgoignesc Gaia Energy Corporation, and the local utility company on a project to bring power to isolated communities in the Northern Marashrra Mountains. The project was a success and it expanded across the western and southern parts of the country. These agrivoltaic projects have been resource intensive because, starting in 2025, Battganuur required them to create or connect to a micro-grid. Since the existing grid was subpar in many rural areas this requirement meant that in many areas entirely new grids were created. While this has slowed the expansion of agrivoltaic projects across the country, it has created a much higher resiliency in the communities where they are install. Agrivoltaics cover 33.7 hectares of farmland and generate around 250MW of power for local communities who were previously underserved or not at all connected to the national power grid.
Battganuur is a pioneer in "vertical agrivoltaics" system, solar cells are oriented vertically on farmland. In 2022, Agricultural University of Maradan State partnered with the Burgoignesc Gaia Energy Corporation piloted a vertical agrivoltaics project with bifacial vertical solar panel (BVSP) array in a corporate latifundia. The pilot proved 3-4% more efficient than the standard horizontal array layout. They were also able to double the total amount of photovoltaic coverage of the of the same acreage. Between 2025-2032 14 hectares of BVSPs were installed representing over 40% of the total agrinergie arrays in Battganuur.
Logging/Mineral extraction

The tropical hardwood forestry is centered in the provinces of Ahabijan, Andivaz, Takand, Maradan, and Malarand. The primary woods cultivated and logged are teak, mahogany, ebony, rosewood, and padauk. Battganuur's timber industry is dominated by large companies employing advanced machinery in well planned plantations. In total, it employs around 320,000 people. Buttganuur logs 3 million tons of teak annually, around 2.5 million tons are exported. This sector employs an estimated 150,000 people directly in cultivation, logging, and processing. 2 million tons of mahogany are logged annually, Battganuur exports around 1.8 million tons. The mahogany sector employs an estimated 120,000 people across various stages of the industry. While Battganuur harvests around 300,000 tons of ebony annually, only 200,000 tons are exported due to strict regulations and conservation efforts. This sector employs approximately 25,000 people, with a focus on responsible harvesting and community involvement. Renowned for its intricate grain and vibrant colors, rosewood cultivation and logging are closely regulated in Battganuur. Large companies cultivate and harvest around 150,000 tons annually, exporting only 100,000 tons due to international restrictions on endangered species. This sector employs around 10,000 people, with a strong emphasis on sustainable practices and ethical sourcing. Known for its reddish-orange hue and durability, padauk cultivation remains limited due to its slower growth rate. Large companies manage smaller plantations, producing around 200,000 tons annually and exporting 150,000 tons. This sector employs around 15,000 people, focusing on research and development for faster-growing padauk varieties while maintaining responsible practices.
West dry tropical area: acacia, neem, and some sal varieties. Sustainable management and focus on value-added products like furniture and veneers would be key.
Southeast: mesquite or acacia, but small scale
Rubber is a key sector in Battganuur's economy. Located in the nation's humid northeast, the provinces of Ahabijan, Andivaz, Takand, Maradan, and Malarand, host massive rubber plantations, managed by both large-scale companies and smaller family farms, thrive under the monsoon rains. While Hevea brasiliensis, the Pará rubber tree, is the king shit. The annual production is 300,000 tons, Battganuur is one of the largest exporters in the global rubber market.
Mining
diamonds
Fishing
Deep Sea Fishing
Fishing on the Kandahar
Aquaculture
Main article: Aquaculture Aquatic life farming, in general
- Pisciculture- fish farming
- Mariculture- Saltwater fish farming
- shrimp farming
- oyster farming
- algaculture
Manufacturing
Nuradaj MILCAR plant

In 2015, MILCAR opened a plant in Nuradaj, Battganuur. This plant builds the passenger variant Jornaleros used by many louage services in the Daria region of Audonia. They plant also includes repair facilities to maintain the buses they build. The plant employees about 1,000 people as is intentionally unautomated as a way to provide employment opportunities. Due to the wage differential between Pelaxia and Battganuur the plant is still profitable for the Pelaxian company.
Infrastructure
-
Louage station
Maritime
Rail
Battganuur uses Standard gauge, 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) as most of its rail infrastructure has been under the auspices of Burgundie and its sphere of influence in the Middle seas region, who all use that rail gauge.
Roads
Louage
A louage is a minibus shared taxi in many parts of Daria that were colonized by Burgundie. In Burgoignesc, the name means "rental." Departing only when filled with passengers not at specific times, they can be hired at stations. Louage ply set routes, and fares are set by the government. In contrast to other share taxis in Audonia, louage are sparsely decorated. Louages use a color-coding system to show customers what type of transport they provide and the destination of the vehicle. Louages with red lettering travel from one state to another, blue travel from city to city within a state, and yellow serves rural locales. Fares are purchased from ticket agents who walk throughout the louage stations or stands. Typical vehicles include: the MILCAR Jornalero, the TerreRaubeuer Valliant 130, and the CTC M237-07.
Air
Energy and electricity
Phone service and internet
See also









































































