Government of Burgundie: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
!34,441,850 | !34,441,850 | ||
!76,171.55 km<sup>2</sup> | !76,171.55 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Alcairet]] | ![[Alcairet]] | ||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
!2,340,630 | !2,340,630 | ||
!23,413.49 km<sup>2</sup> | !23,413.49 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Agiocles]] | ![[Agiocles]] | ||
| Line 157: | Line 157: | ||
!34,441,850 | !34,441,850 | ||
!91,685.579 km<sup>2</sup> | !91,685.579 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Ile Burgundie]] | ![[Ile Burgundie#Province|Ile Burgundie]] | ||
![[Vilauristre]] | ![[Vilauristre]] | ||
!160,377,130 | !160,377,130 | ||
!62,936.711 km<sup>2</sup> | !62,936.711 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
![[ | ![[Ile Burgundie]] | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Alexarmes]] | ![[Alexarmes]] | ||
| Line 171: | Line 171: | ||
!958,310 | !958,310 | ||
!58,430.132 km<sup>2</sup> | !58,430.132 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Montverd]] | ![[Montverd]] | ||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
!12,940,040 | !12,940,040 | ||
!151,358.91 km<sup>2</sup> | !151,358.91 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
!N/A | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 185: | Line 185: | ||
!4,053,140 | !4,053,140 | ||
!1,77,414.19 km<sup>2</sup> | !1,77,414.19 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
!N/A | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
!356,020 | !356,020 | ||
!129,136.81 km<sup>2</sup> | !129,136.81 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Flordeterra]] | ![[Flordeterra]] | ||
| Line 213: | Line 213: | ||
!17,358,130 | !17,358,130 | ||
!129,085 km<sup>2</sup> | !129,085 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Martilles]] | ![[Martilles]] | ||
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
!4,274,370 | !4,274,370 | ||
!69,074.983 km<sup>2</sup> | !69,074.983 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Marves]] | ![[Marves]] | ||
| Line 227: | Line 227: | ||
!6,758,960 | !6,758,960 | ||
!44,496 km<sup>2</sup> | !44,496 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Nauta Normand]] | ![[Nauta Normand]] | ||
| Line 241: | Line 241: | ||
!1,356,020 | !1,356,020 | ||
!131,545.5 km<sup>2</sup> | !131,545.5 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
!The empty one, ya dingus, to the left of Panomes | !The empty one, ya dingus, to the left of Panomes | ||
| Line 248: | Line 248: | ||
!TBD | !TBD | ||
!60,191.324 km<sup>2</sup> | !60,191.324 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
!{{Flag|Sudmoll}} | !{{Flag|Sudmoll}} | ||
| Line 269: | Line 269: | ||
!TBD | !TBD | ||
!118,181.16 km<sup>2</sup> | !118,181.16 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Nostrestran}} | ||
! | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Drusla]] | ![[Drusla]] | ||
| Line 276: | Line 276: | ||
!TBD | !TBD | ||
!27,868.272 km<sup>2</sup> | !27,868.272 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
!N/A | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
![[Faramount | ![[Faramount#province|Province of Faramount]] | ||
!TBD | !TBD | ||
!TBD | !TBD | ||
!308,907.882 km<sup>2</sup> | !308,907.882 km<sup>2</sup> | ||
! | !{{flag|Faramount}} | ||
!N/A | !N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 22:16, 9 February 2024
This article is a work-in-progress because it is incomplete and pending further input from an author. Note: The contents of this article are not considered canonical and may be inaccurate. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. |
Burgundie is a federal crowned republic under the sovereignty of a Great Prince, who in turn, serves the Pacta conventa of The Burgundies. The Government of Burgundie is a Representative democracy, served by congresses at local, provincial, and constituent country level. At the national level the Citizens Court of the National Assembly (Burg. La Assemblee de Ciutadans de l'Assemblee Nacional, ACAN) serves as the highest congress of the land.
All political entities in Burgundie are governed through the concept that all government is local. The layered approach is an important part of Burgoignesc political culture. The sense of civic engagement in government is high.
Administrative Divisions
Municipal Government
Template:Futher Historically municipalities in Burgundie derived their city rights from the rulers of the Kingdom of Dericania (de jure the Emperor of the Levantines), by royal decree. However, as fiefdoms gave way to bourgeois trade hubs the power and rights of municipalities grew and royal charters gave way to popular charters around the 1860s.
| Name | Constituent Country | Population | Municipal classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vilauristre | Ile Burgundie | 8,526,659 | Capital both of Ile Burgundie and the Burgundie |
| Port Diteaux | Ile Burgundie | 5,156,754 | Largest port in Burgundie |
| Reimont Gillete | Duchy of Zelthus | 4,548,495 | Capital of Duchy of Zelthus |
| Stearlinge Arch | Grand Duchy of Dübenneck | 2,436,433 | Capital of the Grand Duchy of Dübenneck |
| Mattiusvale | Burgundie | TBD | Pilgrimage site for the tomb of St. Mattius and the spiritual home of Burgundie |
| Kreckerhavn | Bailiwick of AyerSee | 285,584 | Capital of the Bailiwick of AyerSee |
| Klipperby | Bailiwik of Sturmhavn | 275,834 | Capital of Bailiwik of Sturmhavn |
| Oparo Nui | 3,658 | church/market town or mercirc, capital of Sudmoll | |
| Burgraviate of Wintergen | 754,349 | Capital of Burgraviate of Wintergen | |
| Maarküla | Duchy of Zelthus | 4,583,596 | |
| Bakkajahlíð | Burgundie | 3,767,532 | |
| Eszaby | Burgundie | 2,897,230 | |
| Rødoberga | Burgundie | 658,457 | |
| Drøfest | Grand Duchy of Dübenneck | 1,547,459 | |
| Burgen | Burgundie | 329,564 | |
| Ravenna | Burgraviate of Adtaran | 3,450,600 | Capital of Burgraviate of Adtaran |
| Coryna | Duchy of Pumbria | 2,544,957 | Capital of Duchy of Pumbria |
more to be added ^^^^^^^^
Burgundie has a variety of municipal types. The largest being a city (Burg: metropol), thusly named as historically they hosted a cathedral. These are typically include the pre- or suffixes vil-, -vil, Ville-, or -ville, of Latinic origin meaning farm. Some regional variation is seen in these naming conventions. In Faramount where the Gassavelian people are a historically powerful population -vis, -vit, or -vitham are a common, coming from eastern Audonian languages meaning dwelling or settlement. In parts of central Burgundie where Istroyan influence was strongest, -opol, -oic, and -ocis are likely, coming from Istroyan meaning house.
Below the metropol is the "church/market town" or mercirc in Burgoignesc. These towns typically had or have larger populations and are more densely populated. In rural areas they are often the seat of the sergentie and the paroquiel. These where typically built up around medieval feudal seats and thusly it is common for them to have keeps/castles that now serve either as county administrative offices, niche business parks, or tourist attractions.
The smallest type of municipality is a pravie, meaning an anomaly. These hamlets do not that the population to support a church. They are typically very rural and are purpose built around a niche industry. They became more common in the 19th century, and then again during later 20th century with mass migration to the cities.
County Government
The equivalents of a county in Burgundie are the sergentie and the paroquiel. They are functionally the same and retain their separate names purely as a ceremonial flourish. They exist only in less populated areas, in opposition to free cities, and oversee multi-municipal services and administration. Typical services include policing, fire fighting, public works, and in some extreme cases direct municipal governance. Sergentie and paroquieles are not a representative level of government and do not maintain their own legal status. However, they are the lowest level of government that the national governments will interact with when distributing fiduciary support (e.g. disaster aid, stimulus funding). The lead administrator of a sergentie is called a loctenent (Eng: lieutenant), and the same in a paroquieles is a curat (Eng: rector), their responsibilities include ensuring the day to day functioning of their jurisdiction and as the sole position responsible for liaising with higher levels of government in the event of fiduciary dispensation.
- Error creating thumbnail: File missing Ceremonial dress of a sergoignesc loctenent
- Error creating thumbnail: File missing Ceremonial dress of a paroquial curat
Etymology
Sergentie is the Burgoignesc for Serjeanty, a type of feif wherein non-military service was included in the feudal duties. While, sergenties, feus des eques, socagies, etc. existed simultaneously, sergenties were much more common after feudalism the other terms fell out of use. The term refers to historically secular jurisdictions and with free cities make up the majority of lands in Burgundie.
A parish, (Burg: paroquiel) is roughly equivalent to a county where ecclesiastical states providing frankalmoigne existed until unification. These are, by far, less common.
Provinces
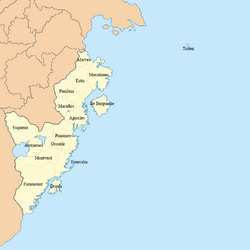
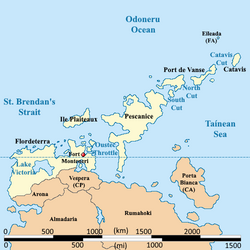
The local administrative body of Burgundie is divided into 31 provinces. They are:
Country Government

Constituent Countries
Stemming from Fiannrian political concepts, Burgundie maintains a constitutional monarchy with representative democracy. The government is regulated by a reformed system of checks and balances defined by the Constitution of Burgundie, which serves as the nations supreme legal document.
In the Burgundian system, citizens are subject to three levels of government: national, provincial, and municipal. The executive and legislative officials are elected by a plurality vote of citizens by county (which also serve as voting districts).
The thalassocratic government is composed of four branches:
Legislative Branch
The Citizens Court of the National Assembly (Burg. La Assemblee de Ciutadans de l'Assemblee Nacional, ACAN) is the unicameral legislator of Burgundie. It makes federal law, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment, by which it can remove sitting members of the government. The Assembly has three seats for each province, one for the Colonial Office, 10 for the clergy, 10 seats reserved for municipal leaders, 10 for a rota of private business leaders and three seats available to foreign interests who would like to be heard. On 6 occasion throughout the year 10 more seats are opened to the public to debate topics that are not on the annual legislative agenda.
While all members can be heard, only the provincial representatives are able to vote on binding laws.
The proceedings of the Assembly are managed by the Sergeant-Parliamentarian and the Sergeant-at-Arms to whom great power is afforded to maintain order and expedient discourse.
Members of the Assembly further divide themselves into various committees and working groups to better address certain issues. The Assembly also maintains its own library, research, and budgetary institutes as well as a small police and intelligence department.
Executive Branch
-
Royal Flag of Burgundie
-
Mantle and Pavilion of Burgundie
-
Crown of Burgundie
-
Palace of the Alvariennes
-
Scepter and orb
-
Palace of the Principality of Faramount
The Court of St. Alphador is the executive branch in Burgundie. The Great Prince is the commander-in-chief of the military, can veto legislative bills before they become law (subject to Golden Council of Ten override), and appoints the members of its Cabinet and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies.
The great prince's cabinet is called the Golden Council of Ten. The Household Guard is technically responsible directly to the Court of St. Alphador, but ostensibly reports to the Chief of Staff of the Army of Burgundie.
Great Prince of Burgundie
Main article: Pasqual I
Crown Prince of Burgundie
Main article: Crown Princess Amelia
Palace of the Alvariennes
Started by ____ in 1729, the Palace of the Alvariennes is considered to be the first Burgoignesc buildings and act of culture as it employed craftsmen from most of modern Burgundie and it was an image to the Derians of the coast and the wealth and culture they had amassed as part of the Burgoignesc colonial empire as separate from the Derians of the interior.
It is named for the Alvarus dynasty whose kingdom encompassed Ile Burgundie, Nostrestran, and parts of coastal Lapody in the 6-10th century.
Judicial Branch
The Lazarine Court is the supreme court of terrestrial Burgundie. It serves as the ultimate legal power in the hierarchy of provincial and municipal courts. The Justices Lazarine are nominated by the Golden Council of Ten, reduced to three candidates and then appointed by the Great Prince. The Lazarine Court sees 30 cases a year, interpret laws, offer legal commentary and overturn unconstitutional laws.
The Maritime Prefecture is the supreme court of maritime Burgundie. It is the ultimate legal power in the legal hierarchy of ship's captains, the Martial Court of the Navy of Burgundie, and any other body dispensing justice in the Burgundian maritime claims. The Commodore Justice is nominated by the Golden Council of Ten, reduced to three candidates and then appointed by the Great Prince. The Maritime Prefecture sees cases, interprets laws, and proposes unconstitutional laws to be overturned by the Lazarine Court. While the Maritime Prefecture is not subordinate to the Lazarine Court, the Consitution of Burgundie is considered a terrestrial document and therefore outside of the jurisdiction of the Commodore Justice. Alternatively, the Lazarine Court is not permitted to pass judgment on cases that will impact Maritime Law without the approval of the Maritime Prefecture. something, something Conservative liberalism
Ministries
Interior
Security Services Bureau
Territorial Cohesion and Relations with Local Government
Transportation and Infractructure
Maritime Administration Agency
- regulating shipping
- awarding subsidies for construction and operation of merchant vessels
- administering subsidy programs
- maintaining the national defense reserve merchant fleet
- setting the curriculum for maritime academies and awarding diploma's/ratings to students who have completed the requirements of graduation
Ecological Transition
External Affairs
Main article: Foreign Relations of Burgundie
Civil Defense and Security
Main Article: Burgoignesc Security Forces
Veterans Services
Overseas Office
Global Improvement
The Global Improvement Branch (GIB-MEA) is the arm of the Ministry of Exterior Affairs tasked with improving the world in terms of how it can positively impact Burgundie. While it is a selfish objective Global Improvement is the branch of government associated with helping to improve global living standards, wages, and reducing/eradicating pandemic diseases. The Branch was created in 1994 to bring together disparate offices and departments from across the Ministry of the Interior, External Affairs, and Revenue that all dealt with improving the lives of those outside of Burgundie.
For a list of programs that the GIB-MEA supports, participates in, and administers see Burgundie's Current Diplomatic Posture.
Economy, Finance, and the Recovery
Internal Revenue
Trade
Satellite Service
The Burgoignesc Satellite Service (Burg: Service Satellit de Burgundie) is an agency of the Department of Trade. It is responsible for the development, research, contracting, launch, and maintenance of the government owned satellites of Burgundie. It is also the regulatory body for private sector satellites. The Agency was formed in the late 1950s as the possibilities of satellite aided navigation on the high seas became more evident and attainable. The program initially set out to create its own independent space program, which is achieved by licensing some Urcean and Fiannrian rocket designs which it hired local firms to create. A launch site was laid out on Port de Vent and initial tests went well. By 1964 it was determined that Burgundie could not keep up with the rapid advance of rocketry development and cancelled its attempts at creating an organic capability, instead signing agreements with Urcea and Fiannria to rent space on their rockets to deliver global positioning system (GPS) satellites, as well as give access to the GPS data. As the precision of satellites increased the goals of Fiannria and Burgundie diverged and Burgundie began to rely more heavily on Urcea. By the mid-1980s the frequency of Burgoignesc satellite launches was 1 in 4 of every Royal Orbital Service and Space Command launch and a more permanent solution needed to be found. A mechanism was created wherein the Burgoignesc Satellite Service was effectively absorbed into the Royal Orbital Service and Space Command. This agreement served as the basis for the agreement that would later create a singular Levantine Union space program.
Using this new collaborative mechanism, in the late 1980s and early 1990s, Burgoignesc astronaut candidates began training in Urcea. In 1994, Flight Commander (Burg: Ale Ijetes) Vincens-Journeay Emersende Draiselle became the first Burgiognac in space. Since that time the astronauts of Burgundie have maintained an almost constant presence on Urcea or international space stations conducting scientific research on behalf of the global community.
The Burgoignesc Satellite Service operates a massive array of mapping, communications, and navigation satellites. The data provided by these satellites are available globally. A smaller number of military observation satellites are maintained, but are part of a wider network of Royal Orbital Service and Space Command military satellites and are not intended to operate independently.
Fair Practice
Labor, Employment and Economic Inclusion
Health and Societal Justice
The health and Equity portfolio oversees the health care public services and the health insurance part of the Social Security of Burgundie, as well as pensions, and civil rights.
Culture
National Education, Youth, and Sport
Higher Education, Research and Innovation
Agriculture and Food
Public Sector Transformation and the Civil Service
Energy
Justice
Emergency Management
Strategic Auxiliary Fleet of the Continuation
The Strategic Auxiliary Fleet of the Continuation is a reserve fleet of steam locomotives train engines, steam ships, and clipper ships maintained by the Ministry of Emergency Management. This fleet is widely distributed across the Burgoignesc Metropole in the event of a nuclear strike. Due to the mechanical nature of these modes of transportation they would not be impacted by an electro-magnetic pulse (EMP) of a nuclear detonation and would be the primary mode of transportation for key royal and national government officials reconstituting or for troop movements.
The rail fleet is maintained by the Army of Burgundie's Army of the Rails and the ship fleet is maintained by Merchant Marine of Burgundie. To maintain operational readiness all of the Strategic Auxiliary Fleet of the Continuation vehicles are used on an at least quarterly basis. The Merchant Marine of Burgundie in particular has found an market with climate conscious consumers and corporate partners and have developed dedicated shipping routes for their Strategic Auxiliary Fleet of the Continuation clipper fleet. In 2032, they even petitioned the Ministry of Emergency Management to build 5 more extreme clippers to maintain a reserve while being able to meet increasing demand.
Environmental concerns have plagued the steam engine and steamer ship programs and there have been a number of scholarships given to universities and think-tanks to come up with a better, equally as accessible, and equally replenishable fuel, instead of coal.
Fleet
- Strategic Auxiliary Fleet of the Continuation trains
- Strategic Auxiliary Fleet of the Continuation ships



























