Istroya Oriental colony: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
As Istroya Oriental expanded, attracting more settlers and intensifying agricultural production, the Audienciæ system faced increasing challenges. The growing complexity of colonial society, coupled with the BRTC’s desire for tighter control over colonial affairs, created tension. The Audienciæ's decentralized structure struggled to manage the expanding colony’s administrative and judicial demands. By the 1620s, the BRTC began to exert increasing influence over the Audienciæ's decisions, limiting its autonomy. This tension continued into the 1630s, with the BRTC gradually appointing a viceroy. | As Istroya Oriental expanded, attracting more settlers and intensifying agricultural production, the Audienciæ system faced increasing challenges. The growing complexity of colonial society, coupled with the BRTC’s desire for tighter control over colonial affairs, created tension. The Audienciæ's decentralized structure struggled to manage the expanding colony’s administrative and judicial demands. By the 1620s, the BRTC began to exert increasing influence over the Audienciæ's decisions, limiting its autonomy. This tension continued into the 1630s, with the BRTC gradually appointing a viceroy. | ||
===Viceroyalty=== | ===Viceroyalty=== | ||
The appointment of a viceroy in | The appointment of a viceroy in [[1637]] resulted from the [[Duchy of Bourgondi]]'s rapidly expanding colonial empire, increased intercolonial warfare, conflicts with rival colonial powers like Kiravia on the high seas, and the desire for colonial self-sufficiency and profitability. Centralizing authority under direct BRTC control via a viceroy in each colony, including Istroya Oriental, gave the Duke greater military control and enhanced financial and military strategy. The viceroy held supreme executive, legislative, and judicial power, streamlining colonial administration and implementing BRTC policies. This facilitated more efficient resource extraction and management, particularly within the expanding plantation economy. However, it diminished the Audienciæ’s previous local autonomy, creating friction with colonists. The viceroys focused on colonial expansion, increased agricultural output primarily through enslaved labor, and strengthened the BRTC’s economic dominance. This period saw large latifundii consolidate and the slave trade grow. As the colony expanded throughout the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the viceroy’s responsibilities increased significantly. Managing the vast territory, complex economy, and diverse population became unsustainable for a single individual. In [[1761]], the viceroyalty was replaced by presidencies, each governing a distinct region of Istroya Oriental and reporting to a newly established colonial council. | ||
List of Viceroys: | List of Viceroys: | ||
* Guilhem-Piere Andrieu de Tolosie ([[1637]]-[[1652]]) | |||
* Raimon-Jausep Frances de Montpelhier ([[1652]]-[[1668]]) | |||
* Bertrand-Piere Jacmenon Carcasseu ([[1668]]-[[1685]]) | |||
* Folquet-Andrieu Raimon de Narbone ([[1685]]-[[1701]]) | |||
* Isarn-Joan Bernat d'Avinhon ([[1701]]-[[1718]]) | |||
* Aimeric-Bernat Raimon d'Ais ([[1718]]-[[1735]]) | |||
* Uc-Peire Anton Bordeu ([[1735]]-[[1752]]) | |||
* Jaufre-Raimon Bernat de Peiregord ([[1752]]-[[1761]]) | |||
===Presidencies=== | ===Presidencies=== | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 11 January 2025
| This article is a stub. You can help IxWiki by expanding it. |
Istroya Oriental Colony Colonie Istroya Orientale | |
|---|---|
| 1611-1795 | |
|
Flag | |
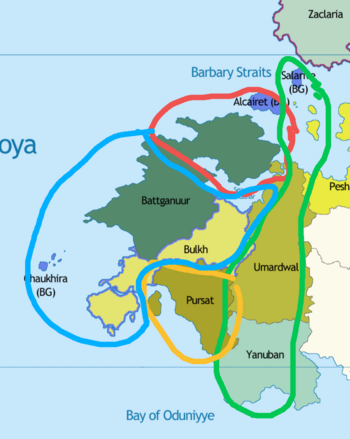 Istroya Oriental Colony in blue Kandahari-Pukhtun colony in green Eloillette in gold Barbary Straits colony in red | |
| Status | Colony of the Duchy of Bourgondi |
| Official language | Burgoignesc |
| Religion | Calvinism/Congregational church, Presbyterianism |
| Government | Constitutional monarchy |
| Governor Epistates | |
| Historical era | Age of Discovery, Age of Sail |
• Established | 1577 |
• Disestablished | 1795 |
| Today part of | Battganuur Bulkh Chaukhira |
Istroya Oriental Colony was a colonial holding of the Duchy of Bourgondi administered by the Bourgondii Royal Trading Company (BRTC) on the western coast of the Audonian region of Daria from 1577 until 1795 at which point the Great Rebellion of Slavery Bay overwhelmed the colony forcing its end and the expulsion of the Occidentals living within it.
Colonial administration
Early administration
The first Audienciæ della Colonie Istroya Oriental was established shortly after the 1577 founding, consisted of a BRTC-appointed magistrate and elected congregational elders. It served as the colony’s highest court, applying Burgoignesc law while considering the unique circumstances and values of the Pharisee settlers. The Audienciæ resolved disputes, ensuring religious freedom, and maintaining order. Beyond its judicial functions, the Audienciæ played a vital role in colonial administration. It advised the BRTC’s appointed governor on policy, managed colonial resources, and collaborated with local congregations and patroons to create local laws. Early Istroya Oriental focused on establishing settlements, developing agriculture, and establishing trade relationships with indigenous Battganuuris. The Audienciæ oversaw land distribution, regulated trade, and managed relations with local tribes. This period saw the growth of key settlements along the coast and the development of plantation agriculture. As Istroya Oriental expanded, attracting more settlers and intensifying agricultural production, the Audienciæ system faced increasing challenges. The growing complexity of colonial society, coupled with the BRTC’s desire for tighter control over colonial affairs, created tension. The Audienciæ's decentralized structure struggled to manage the expanding colony’s administrative and judicial demands. By the 1620s, the BRTC began to exert increasing influence over the Audienciæ's decisions, limiting its autonomy. This tension continued into the 1630s, with the BRTC gradually appointing a viceroy.
Viceroyalty
The appointment of a viceroy in 1637 resulted from the Duchy of Bourgondi's rapidly expanding colonial empire, increased intercolonial warfare, conflicts with rival colonial powers like Kiravia on the high seas, and the desire for colonial self-sufficiency and profitability. Centralizing authority under direct BRTC control via a viceroy in each colony, including Istroya Oriental, gave the Duke greater military control and enhanced financial and military strategy. The viceroy held supreme executive, legislative, and judicial power, streamlining colonial administration and implementing BRTC policies. This facilitated more efficient resource extraction and management, particularly within the expanding plantation economy. However, it diminished the Audienciæ’s previous local autonomy, creating friction with colonists. The viceroys focused on colonial expansion, increased agricultural output primarily through enslaved labor, and strengthened the BRTC’s economic dominance. This period saw large latifundii consolidate and the slave trade grow. As the colony expanded throughout the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the viceroy’s responsibilities increased significantly. Managing the vast territory, complex economy, and diverse population became unsustainable for a single individual. In 1761, the viceroyalty was replaced by presidencies, each governing a distinct region of Istroya Oriental and reporting to a newly established colonial council.
List of Viceroys:
- Guilhem-Piere Andrieu de Tolosie (1637-1652)
- Raimon-Jausep Frances de Montpelhier (1652-1668)
- Bertrand-Piere Jacmenon Carcasseu (1668-1685)
- Folquet-Andrieu Raimon de Narbone (1685-1701)
- Isarn-Joan Bernat d'Avinhon (1701-1718)
- Aimeric-Bernat Raimon d'Ais (1718-1735)
- Uc-Peire Anton Bordeu (1735-1752)
- Jaufre-Raimon Bernat de Peiregord (1752-1761)
Presidencies
Gallery
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
